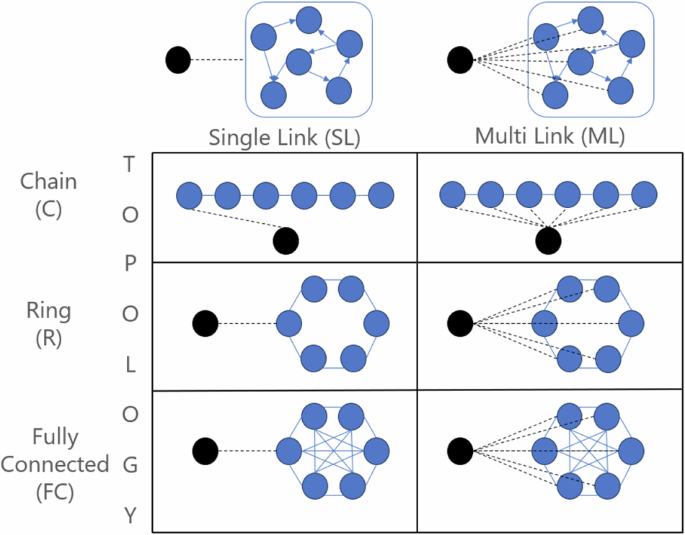
Quantum Extreme Learning Machines (QELMs) leverage untrained quantum dynamics to efficiently process information encoded in input quantum states, avoiding the high computational cost of training more complicated nonlinear models.
On the other hand, Quantum Information Scrambling (QIS) quantifies how the spread of quantum information into correlations makes it irretrievable from local measurements.
Researchers have explored the tight relation between QIS and the predictive power of QELMs.
In particular, they showed efficient state estimation is possible even beyond the scrambling time, for many different types of dynamics, and that in all the cases they studied, the reconstruction efficiency at long interaction times matches the optimal one offered by random global unitary dynamics.
These results offer promising venues for robust experimental QELM-based state estimation protocols, as well as providing novel insights into the nature of QIS from a state estimation perspective.
npj Quantum Information, Published online: 03 February 2025; doi:10.1038/s41534-024-00927-5