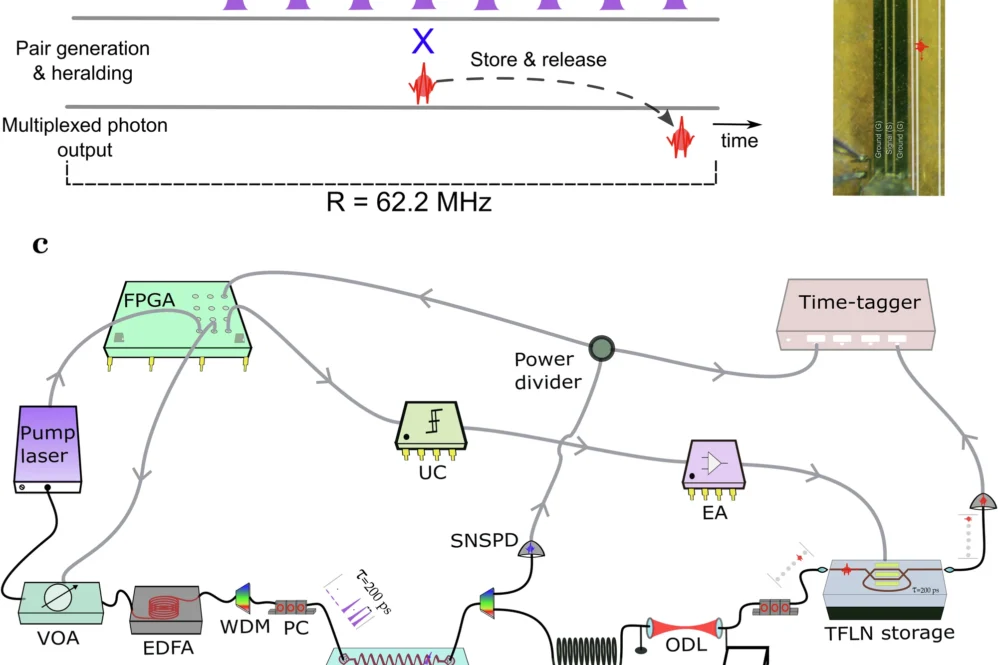
Efficient single-photon generation remains a big challenge in quantum photonics. A promising approach to overcome this challenge is to employ active multiplexing—repeating a nondeterministic photon pair generation process across orthogonal degrees of freedom and exploiting heralding to actively route the heralded photon to the desired single output mode via feedforward.
The main barriers of multiplexing schemes, however, are minimizing resource requirements to allow scalability and the lack of availability of high-speed, low-loss switches.
Researchers have presented in a paper published in npj Quantum Information an on-chip temporal multiplexing scheme utilizing Thin-Film Lithium Niobate (TFLN) photonics to effectively address these challenges.
This time-multiplexed source, operating at a rate of 62.2 MHz, enhances single-photon probability by a factor of 3.37 ± 0.05 without introducing additional multi-photon noise.
This demonstration highlights the feasibility and potential of TFLN photonics for large-scale complex quantum information technologies.
npj Quantum Information, Published online: 06 February 2025; doi:10.1038/s41534-024-00929-3