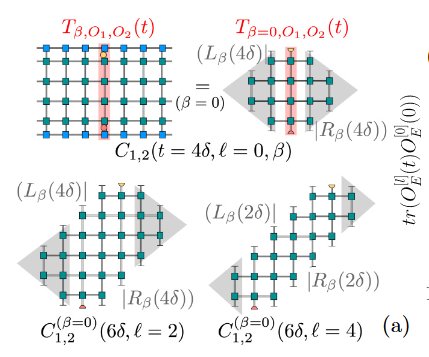
The transverse folding algorithm [M. C. Bañuls et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 240603 (2009)] is a tensor network method to compute time-dependent local observables in out-of-equilibrium quantum spin chains that can overcome the limitations of matrix product states when entanglement grows slower in the time than in the space direction.
This paper, published in Physical Review B, presents a contraction strategy that makes use of the exact light cone structure of the tensor network representing the observables.
The strategy can be combined with the hybrid truncation proposed for global quenches by Hastings and Mahajan Phys. Rev. A 91, 032306 (2015), which significantly improves the efficiency of the method.
The scientists demonstrated the performance of this transverse light cone contraction also for transport coefficients, and discuss how it can be extended to other dynamical quantities.
Read more.