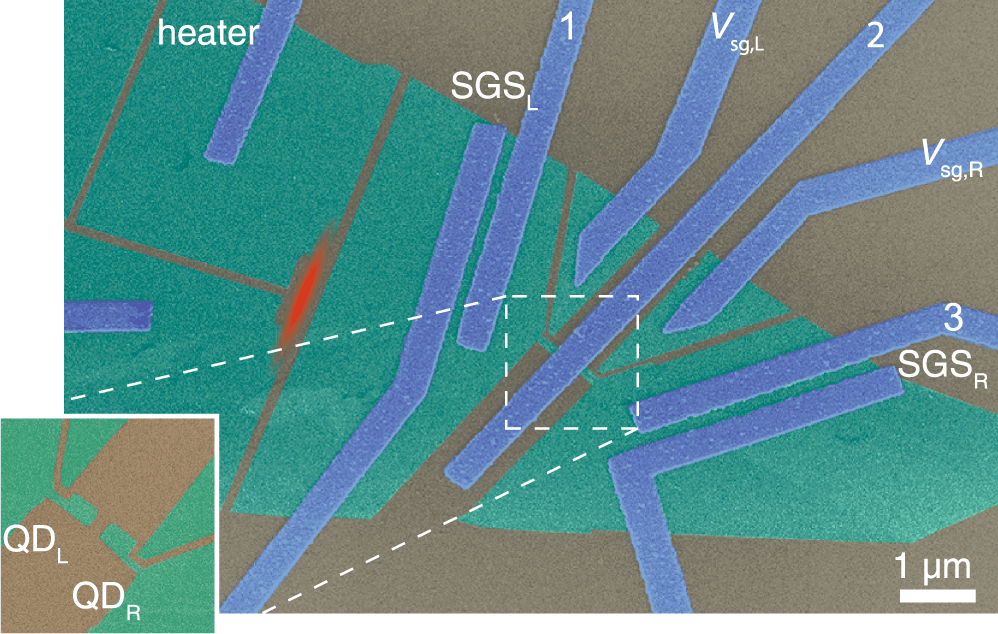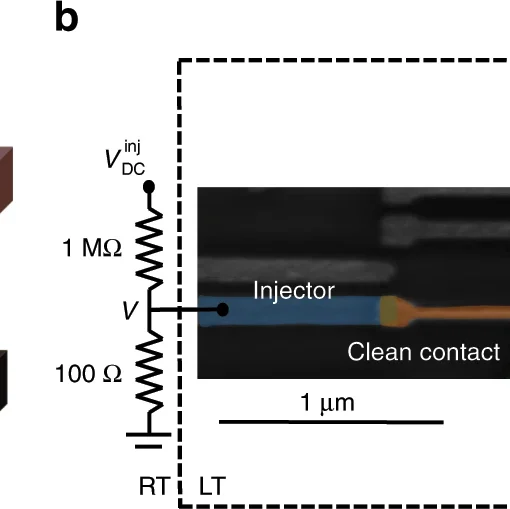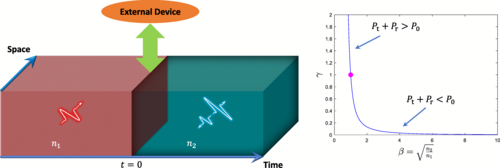
Quantum Light at Time Interfaces: Engineering the Photon Frontier
Time interfaces in materials with suddenly changing refractive indices create unique quantum optical phenomena including photon-pair production and destruction, tunable photon statistics, and opportunities for quantum state engineering.