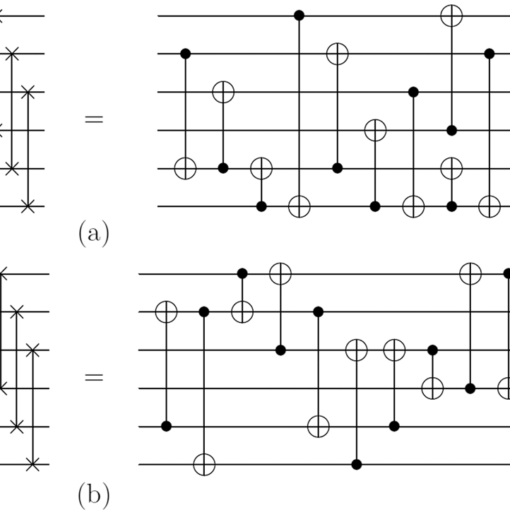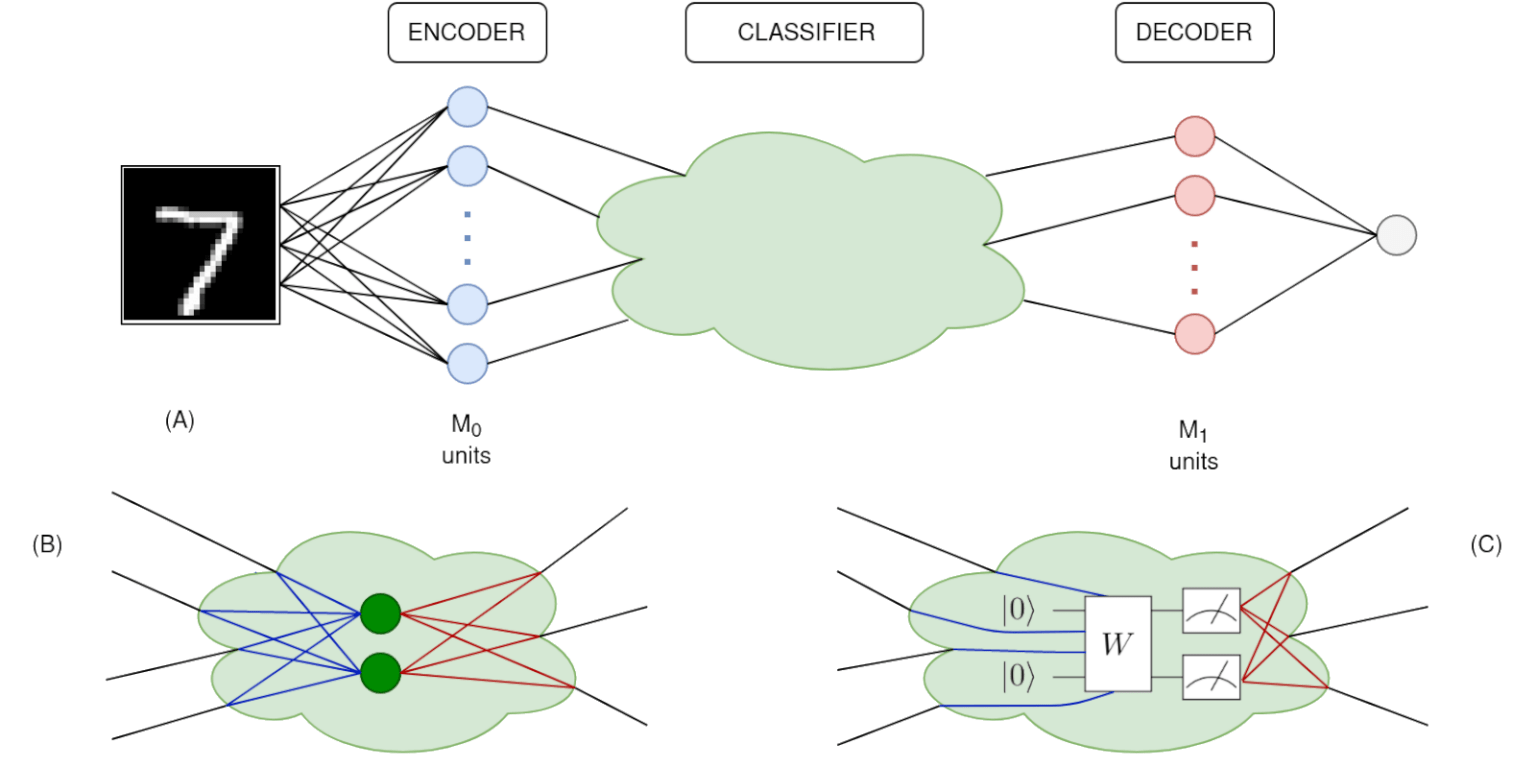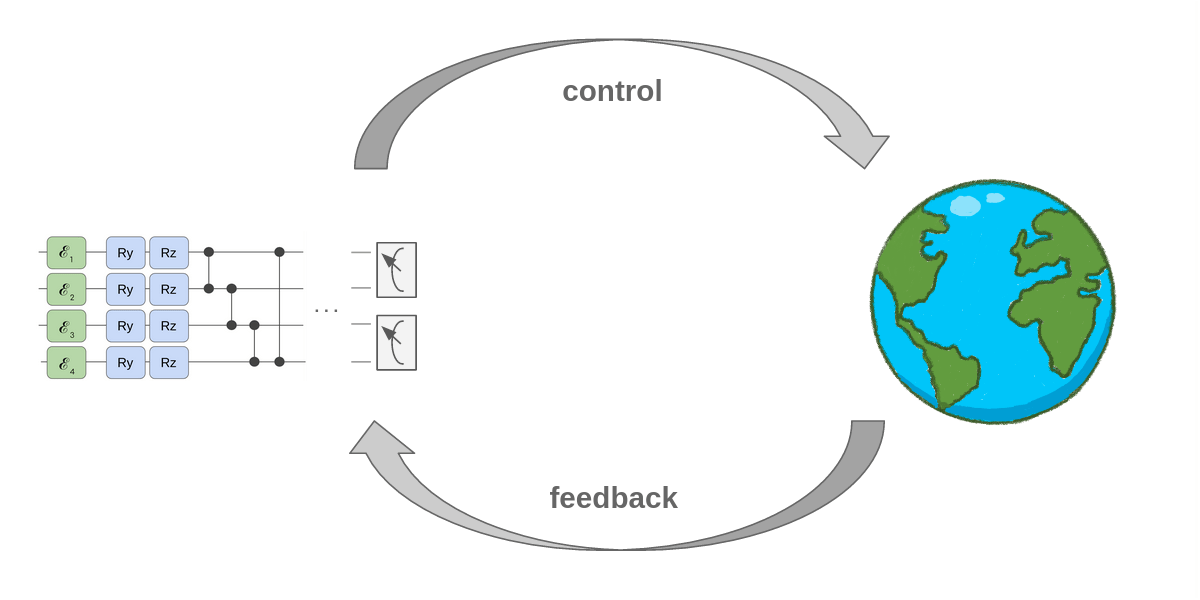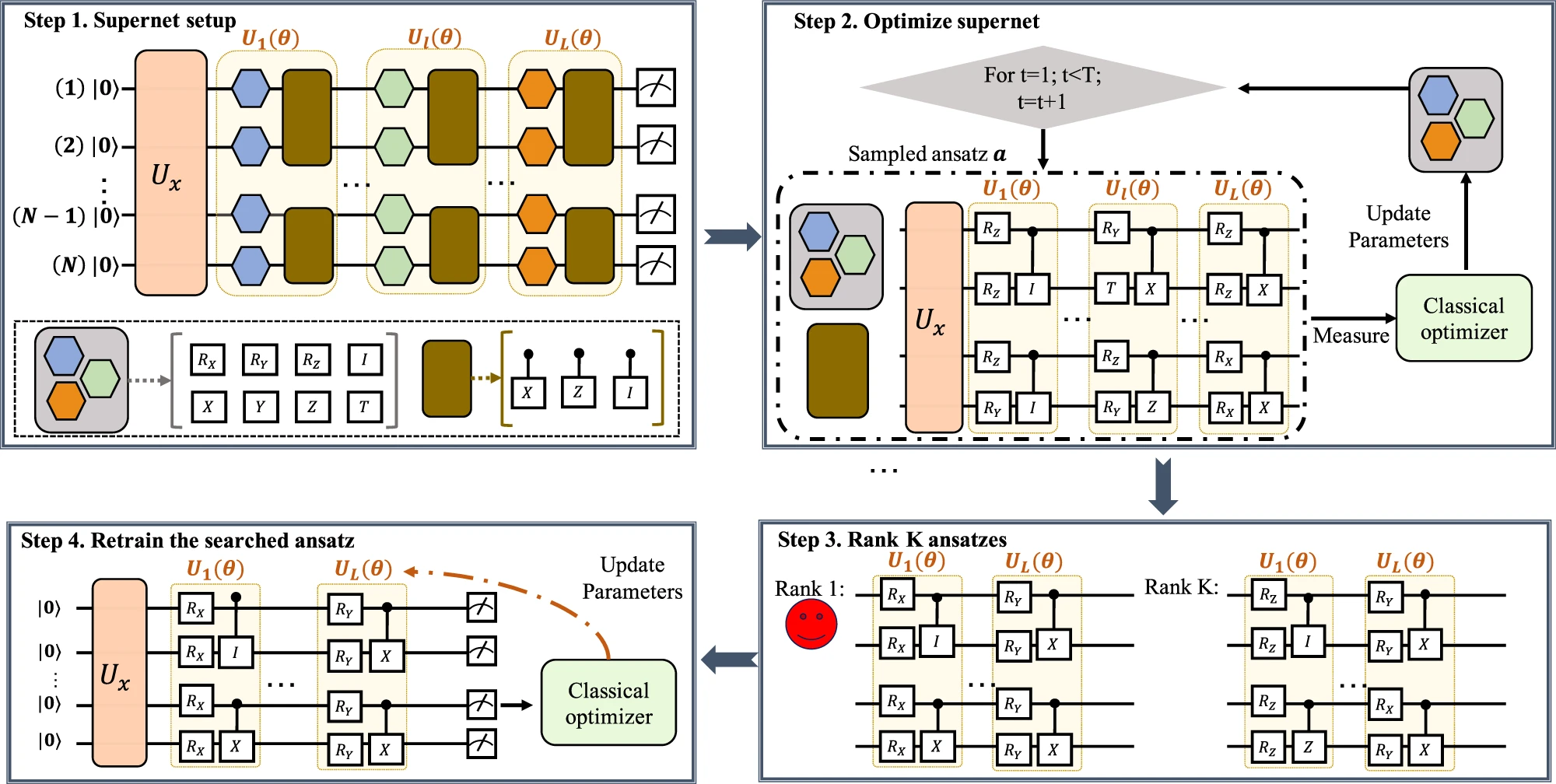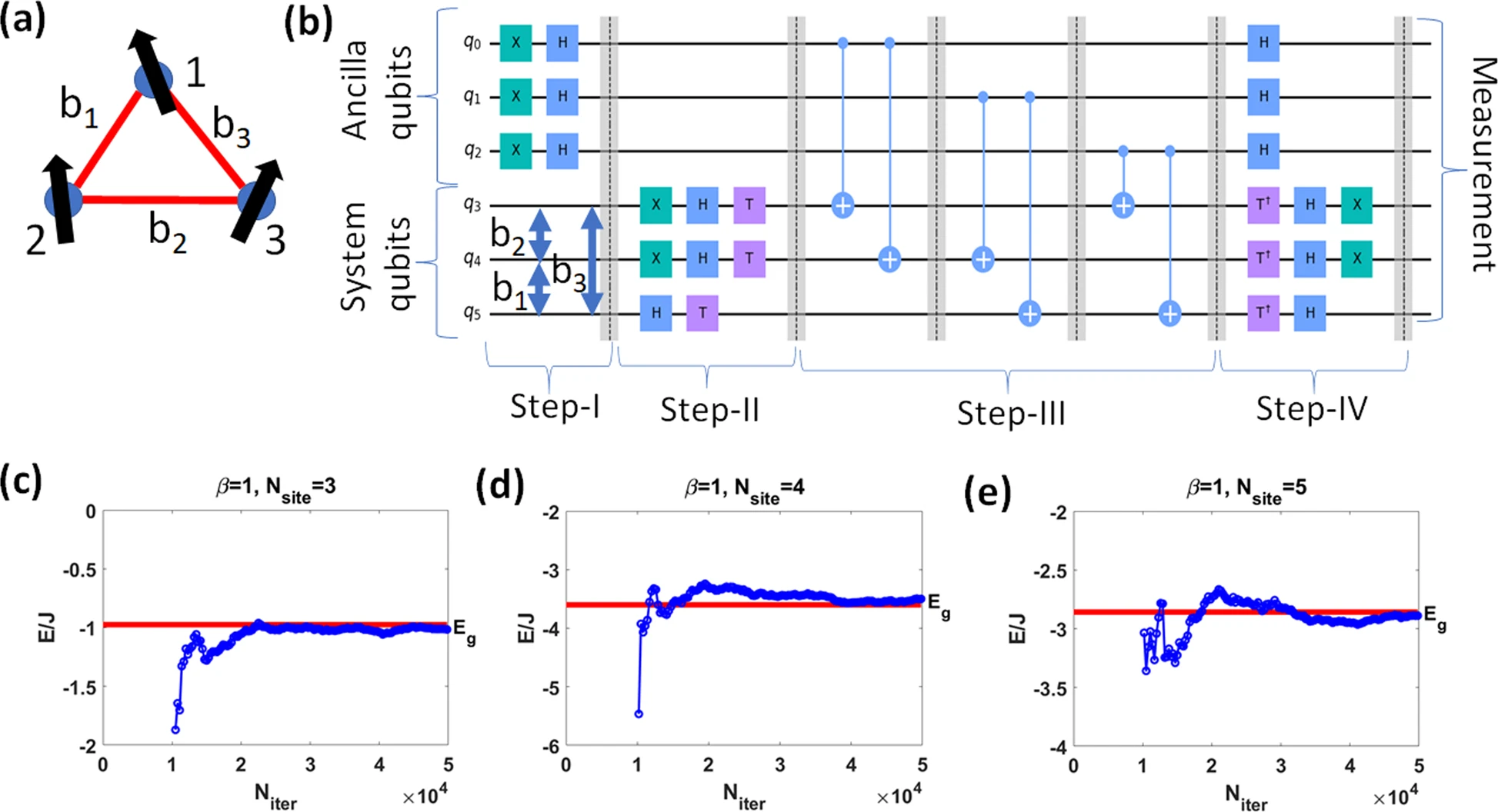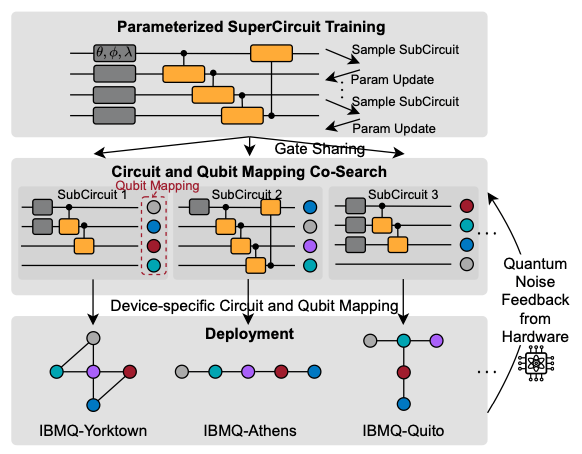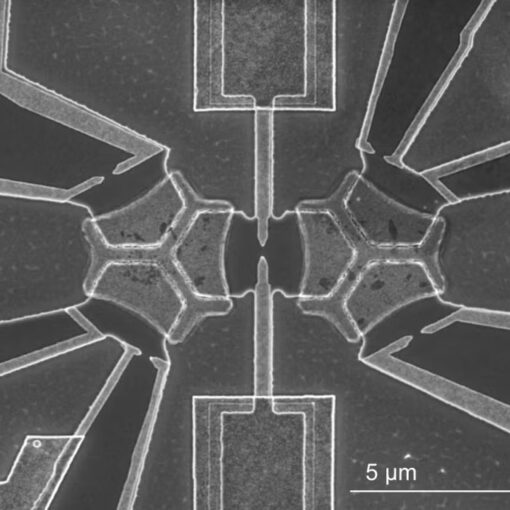
Researchers take a step toward novel quantum simulators
Some of the most exciting topics in modern physics, such as high-temperature superconductors and some proposals for quantum computers, come down to the exotic things that happen when these systems hover between two quantum states.