
The entanglement advantage
Researchers have demonstrated a way to entangle atoms to create a network of atomic clocks and accelerometers. The method has resulted in greater precision in measuring time and acceleration.
By visiting our site, you agree to our privacy policy regarding cookies, tracking statistics, etc.

Researchers have demonstrated a way to entangle atoms to create a network of atomic clocks and accelerometers. The method has resulted in greater precision in measuring time and acceleration.
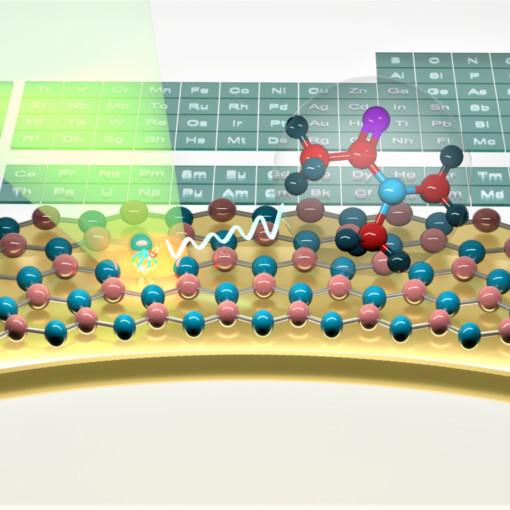
Australian scientists have developed a groundbreaking quantum microscope that uses atomically thin hexagonal boron nitride layers instead of traditional bulky crystals, enabling unprecedented imaging of electric currents, magnetic fields, and single molecules while simultaneously mapping temperature distributions under ambient conditions.
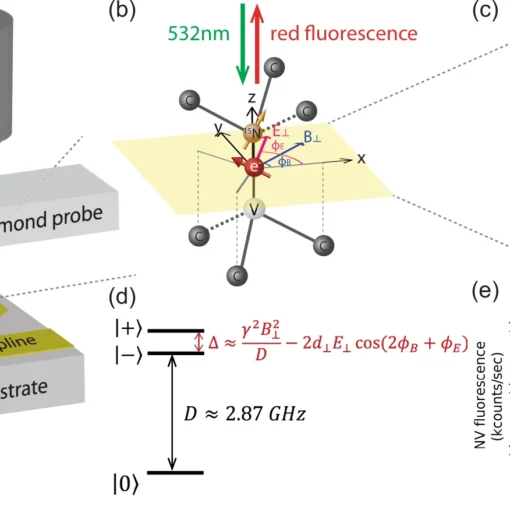
A team of researchers successfully developed a scanning probe quantum sensor using a single nitrogen-vacancy center at a diamond tip that can image both AC and DC electric fields at nanoscale resolution under ambient conditions, achieving sensitivities two orders of magnitude better than previous attempts and overcoming electric field screening through mechanical oscillation techniques.
Quantum clocks are shrinking, thanks to new technologies developed at the UK Quantum Technology Hub Sensors and Timing. Working in collaboration with and partly funded by the UK’s Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (Dstl), a team of […]
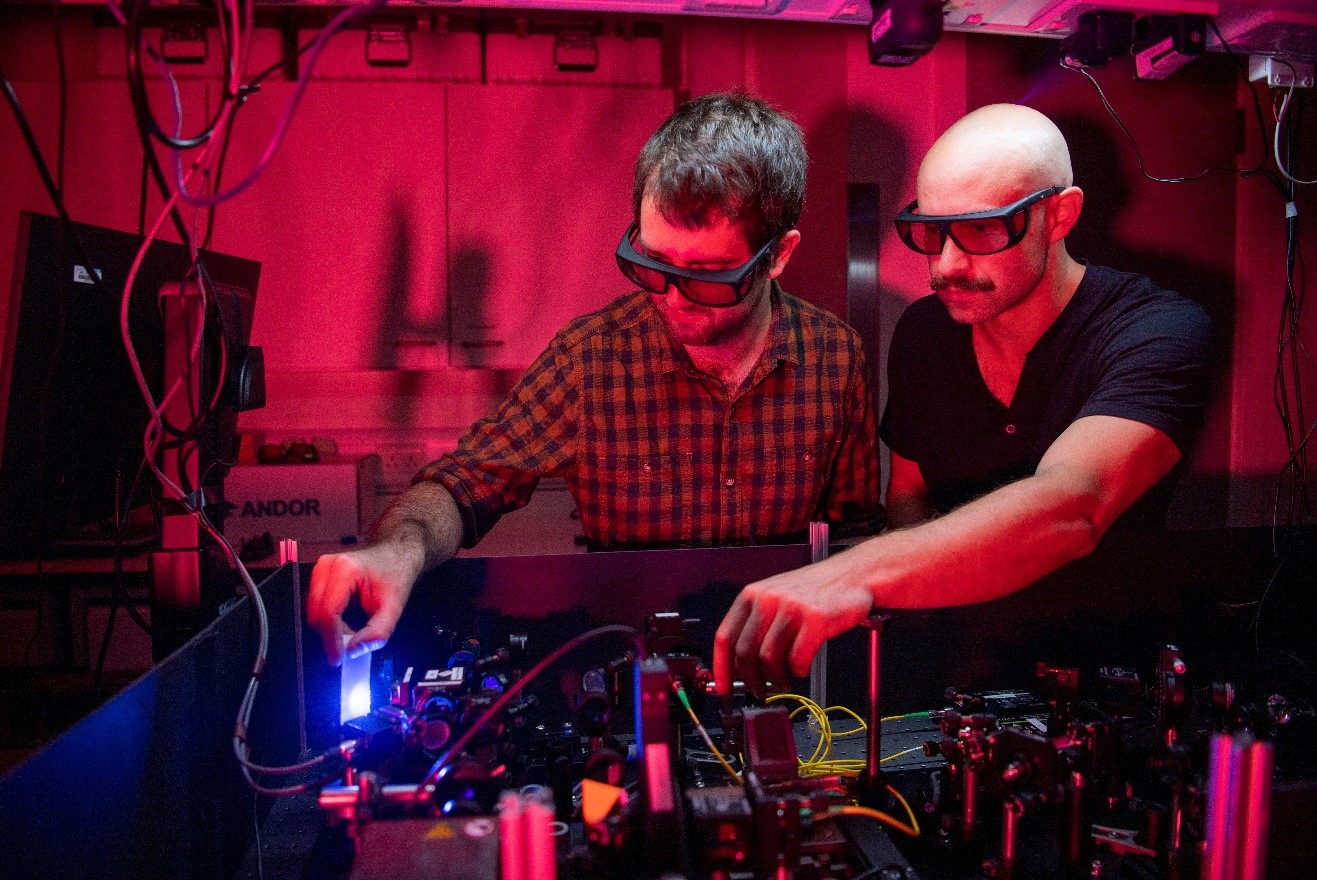

Researchers have shown that a quantum-inspired technique can be used to perform LiDAR imaging with a much higher depth resolution than is possible with conventional approaches. LiDAR, which uses laser pulses to acquire 3D information […]
Researchers at MIT developed a method to enable quantum sensors to detect any arbitrary frequency, with no loss of their ability to measure nanometer-scale features. Quantum sensors detect the most minute variations in magnetic or […]
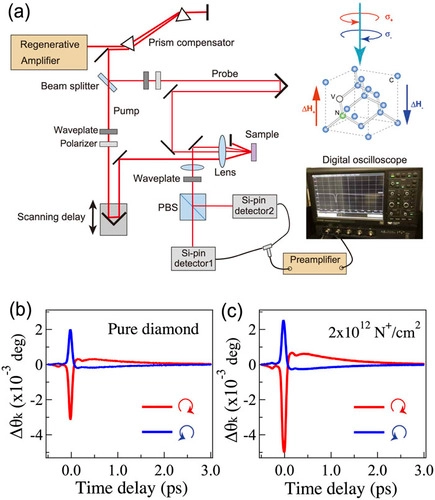
Researchers at University of Tsukuba measured tiny magnetic fields with unprecedented speed. By monitoring spins at Nitrogen-Vacancy (NV) centers along using ultrafast spectroscopy. They hence demonstrated how ultrafast spectroscopy can be used to improve the […]

Dr Anna Kowalczyk, Assistant Professor at the University of Birmingham’s Centre for Human Brain Health, is one of 15 researchers awarded funding from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) to tackle key quantum […]
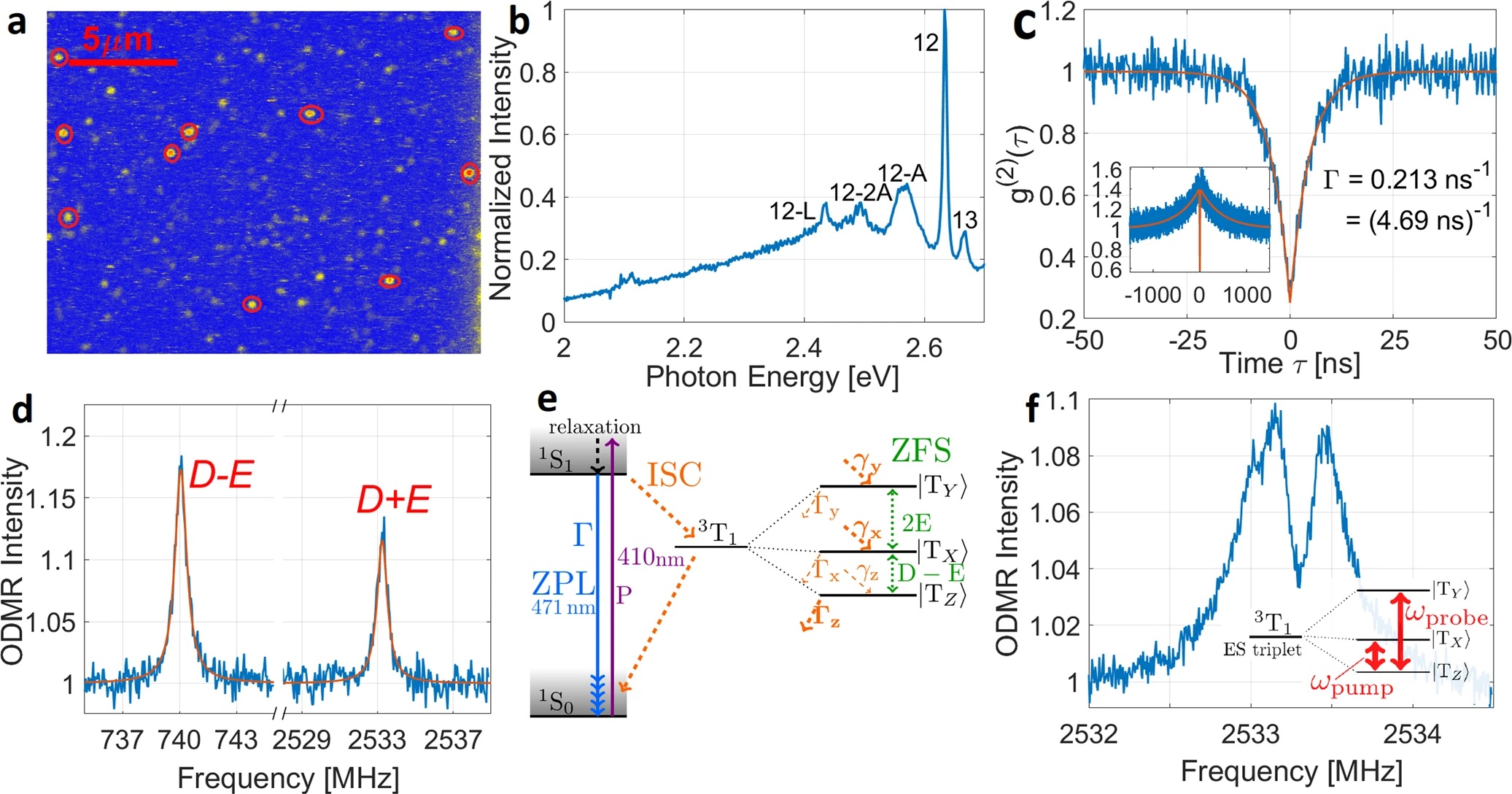
Extending the field of quantum metrology i.e., magnetometry, electrometry, and thermometry to the atomic scale requires robust sensors with high sensitivity and spatial resolution. Optically addressable spins in diamond are excellent candidates as they often […]
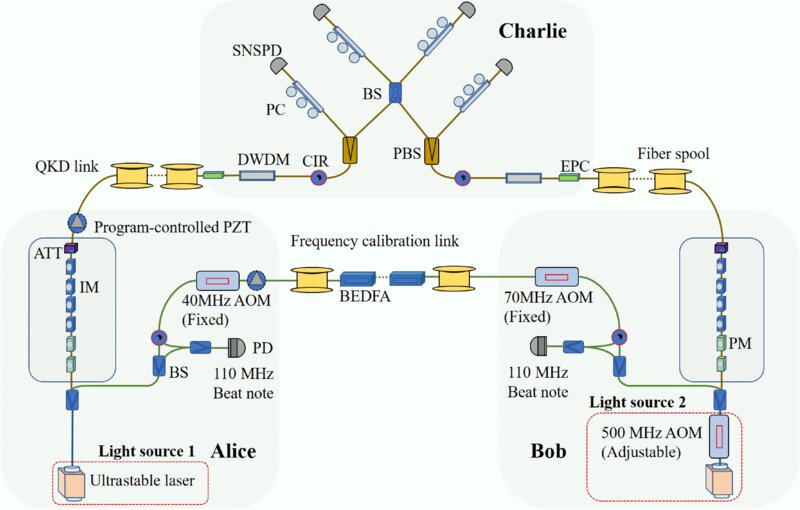
A team of researchers affiliated with several institutions in China has found that Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) networks can be used to accurately measure ground vibration. They have implemented a twin-field, fiber-based QKD network over […]
A team of researchers has built an intelligent sensor—the size of about 1/1000 of the cross-section of a human hair—that can simultaneously detect the intensity, polarization and wavelength of light, tapping into the quantum properties […]

A new project undertaken by a University of Birmingham researcher at the UK Quantum Technology Hub Sensors and Timing along with colleagues in the School of Engineering will help to facilitate greater sustainability for future […]

A team of physicists from the University of Glasgow and Heriot-Watt University have found a new way to create detailed microscopic images under conditions which would cause conventional optical microscopes to fail. They have managed […]
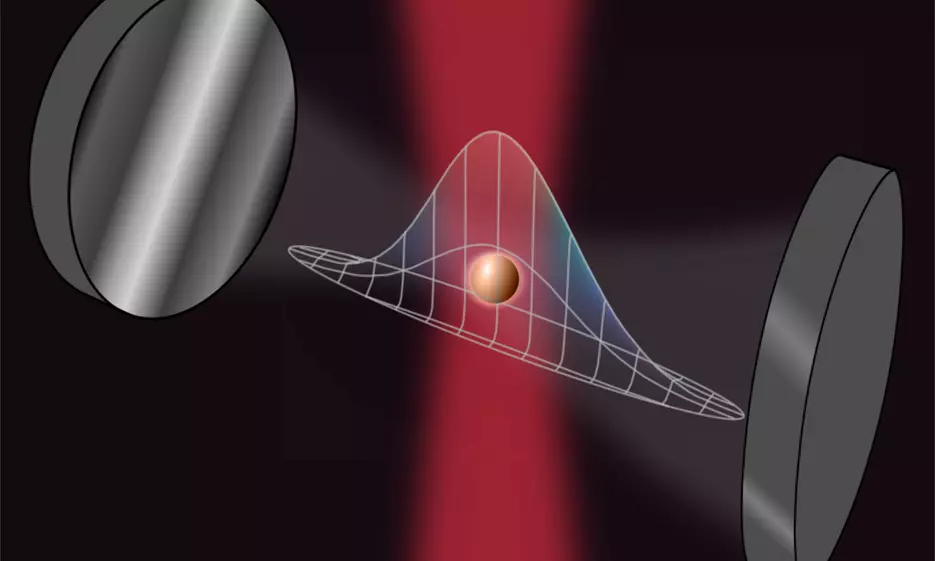
Researchers are now demonstrating how nanoparticles in tiny optical resonators can be transferred into quantum regime and used as high-precision sensors. The team has proposed a new concept for a high-precision quantum sensor. The researchers […]
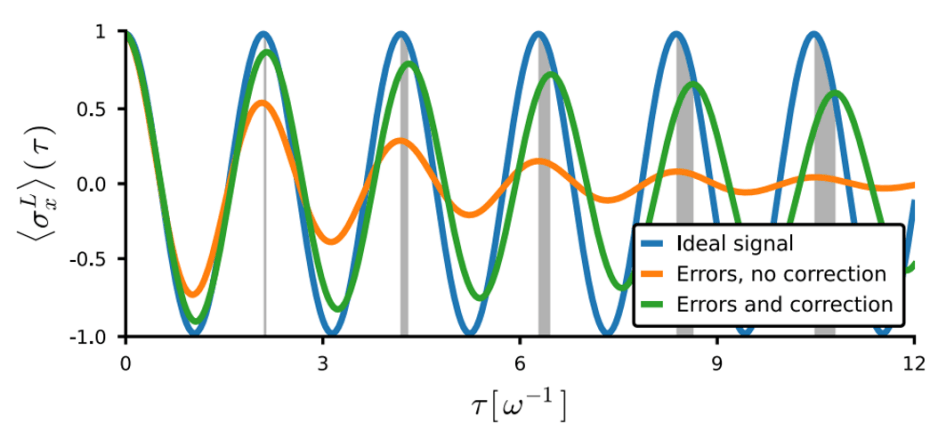
It is well established that quantum error correction can improve the performance of quantum sensors. But new theory work cautions that, unexpectedly, the approach can also give rise to inaccurate and misleading results — and […]
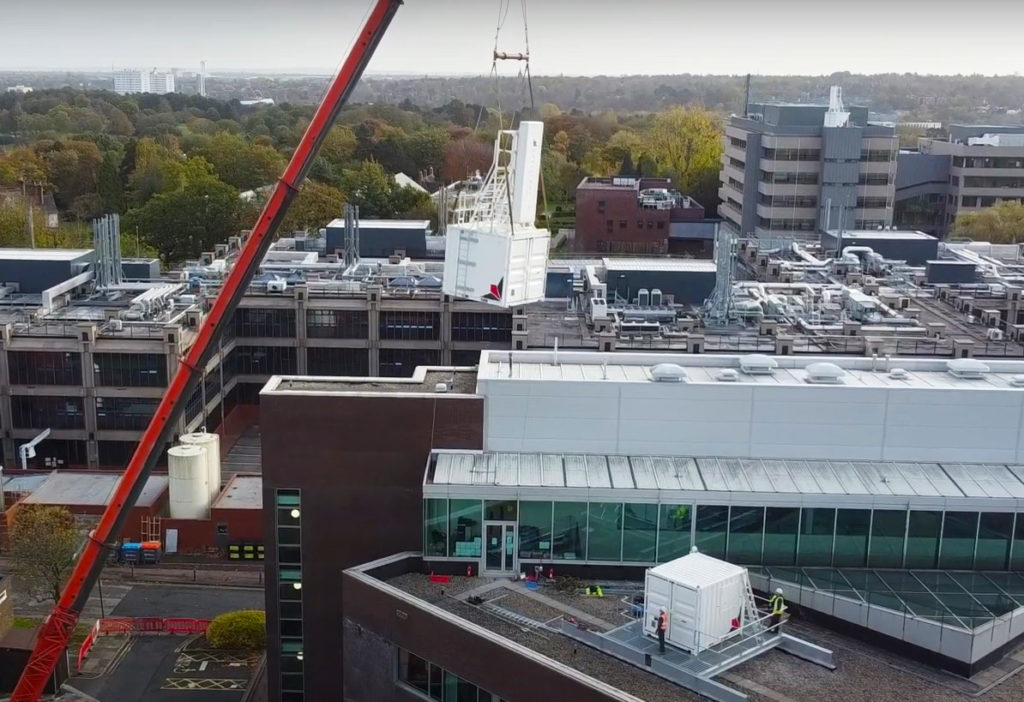

Exactly one year after the first staring radar was installed at the University of Birmingham campus, a second identical radar has been installed, representing another step in the journey to hosting the very first quantum-enabled […]

Two teams of physicists at University of Innsbruck have designed the first programmable quantum sensor, and tested it in the laboratory. To do so they applied techniques from quantum information processing to a measurement problem. […]
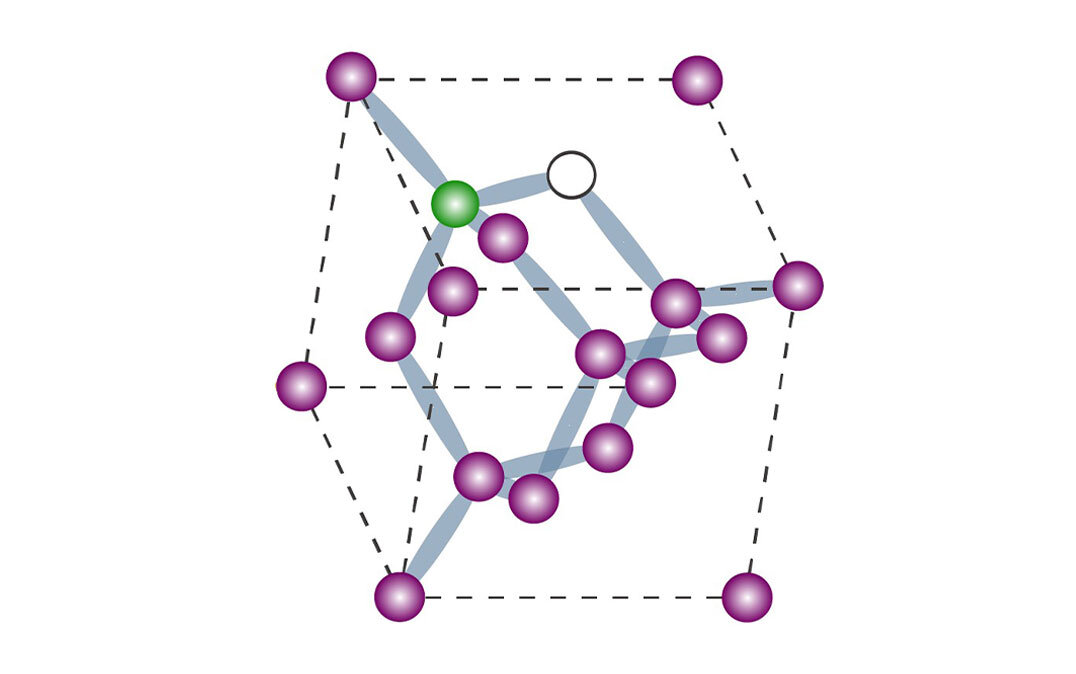
Scientists at the University of Tsukuba have developed a method for monitoring the temperature using the naturally occurring atom-like defects in diamonds. They found that increased heat led to reduced intensity of the nonlinear harmonic […]

A team of scientists at CERN led by MPQ physicist Masaki Hori has found that a hybrid antimatter-matter atom behaves in an unexpected way when submerged in superfluid helium. The result may open a new […]

A new International Network set up by QT Hub Sensors and Timing researchers at the University of Birmingham aims to tackle global challenges, as set out in the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Since the set […]

Bosch is setting up a new business unit to commercialise quantum sensors. Located in Germany initially, it will look to pool the results of research so far and translate them into products. Bosch said that […]
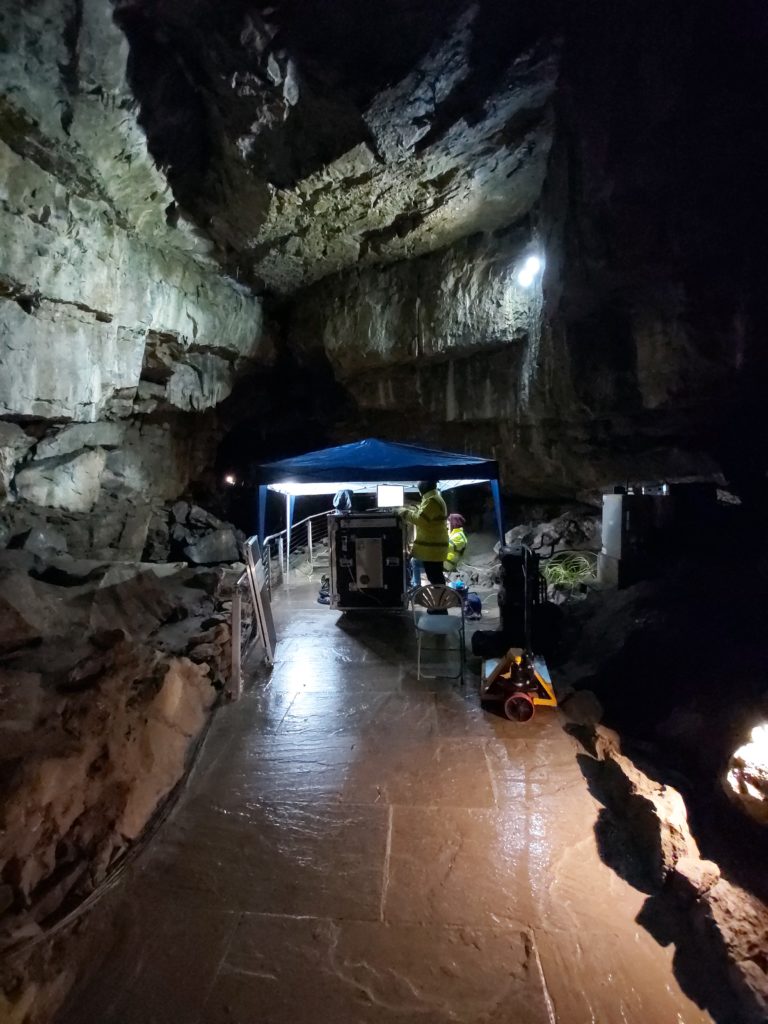

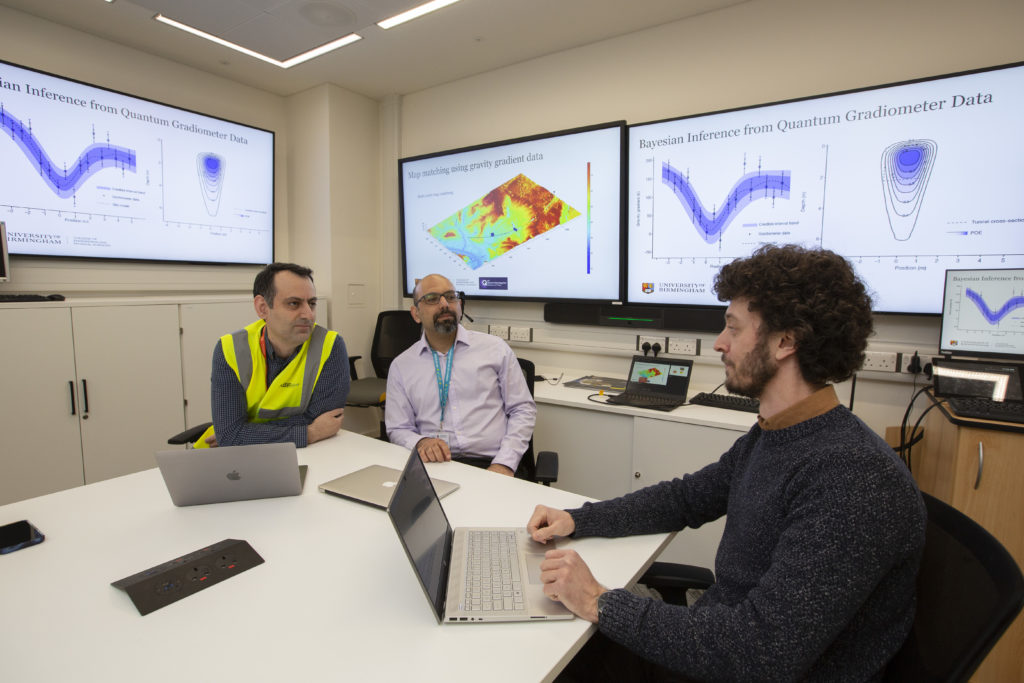
An object hidden below ground has been located using quantum technology – a long-awaited milestone with profound implications for industry, human knowledge and national security. UK National Quantum Technology Hub in Sensors and Timing researchers […]
Deploying quantum technologies in space, while complex, will be truly transformative on a global scale. The International Network in Space Quantum Technologies (INSQT) is a new project led by UK Quantum Technology Hub Sensors and […]
The International Clock and Oscillator Networking (ICON) project has been awarded £1.5 million in funding from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) to bring together world-leading transportable optical clocks and world-leading optical link […]
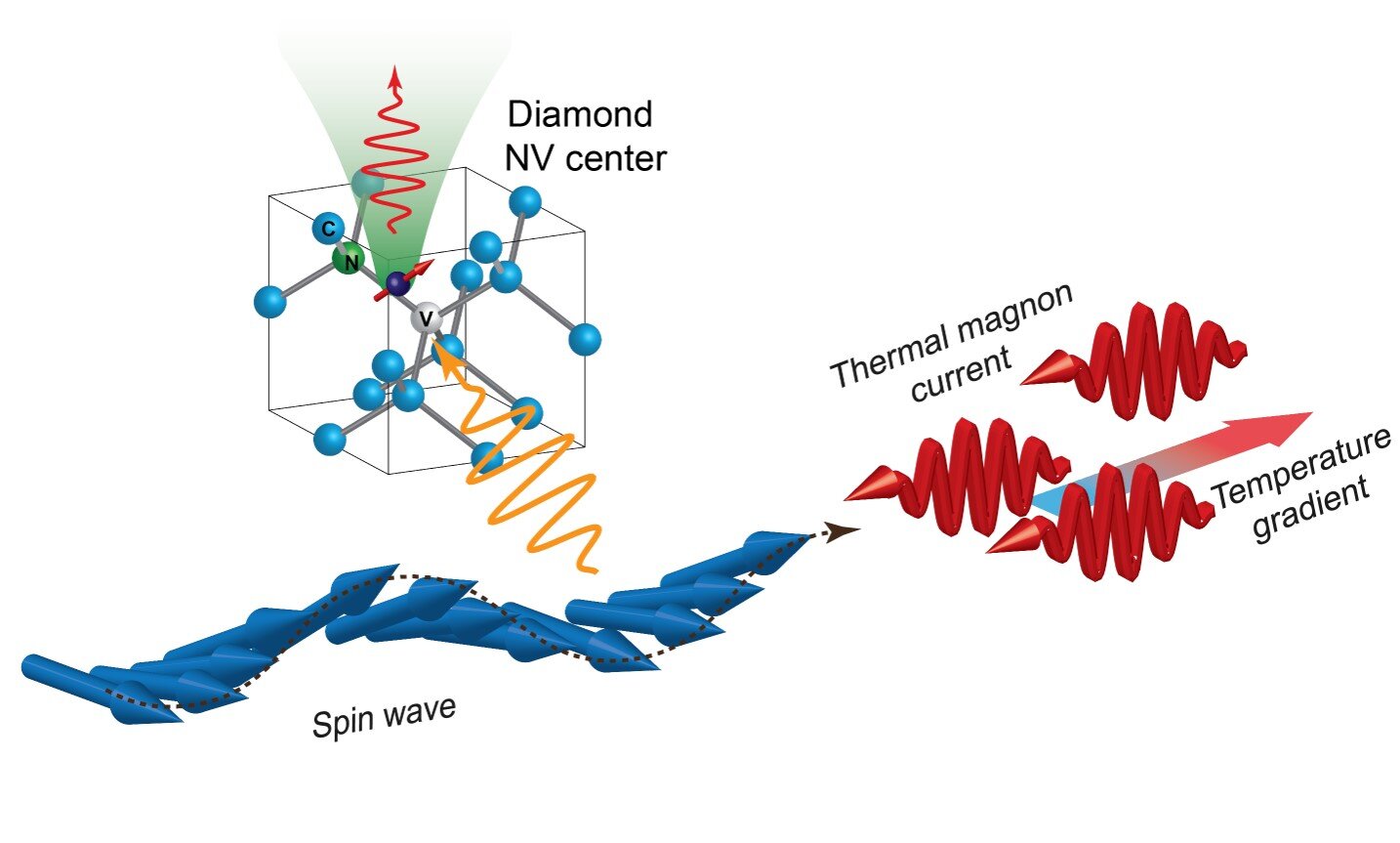
Within the field of spintronics, devices based on the interaction between spin and heat flow have emerged as a potential candidate for new thermoelectric devices (devices which convert heat to electricity). “Magnons,” quanta of spin […]
