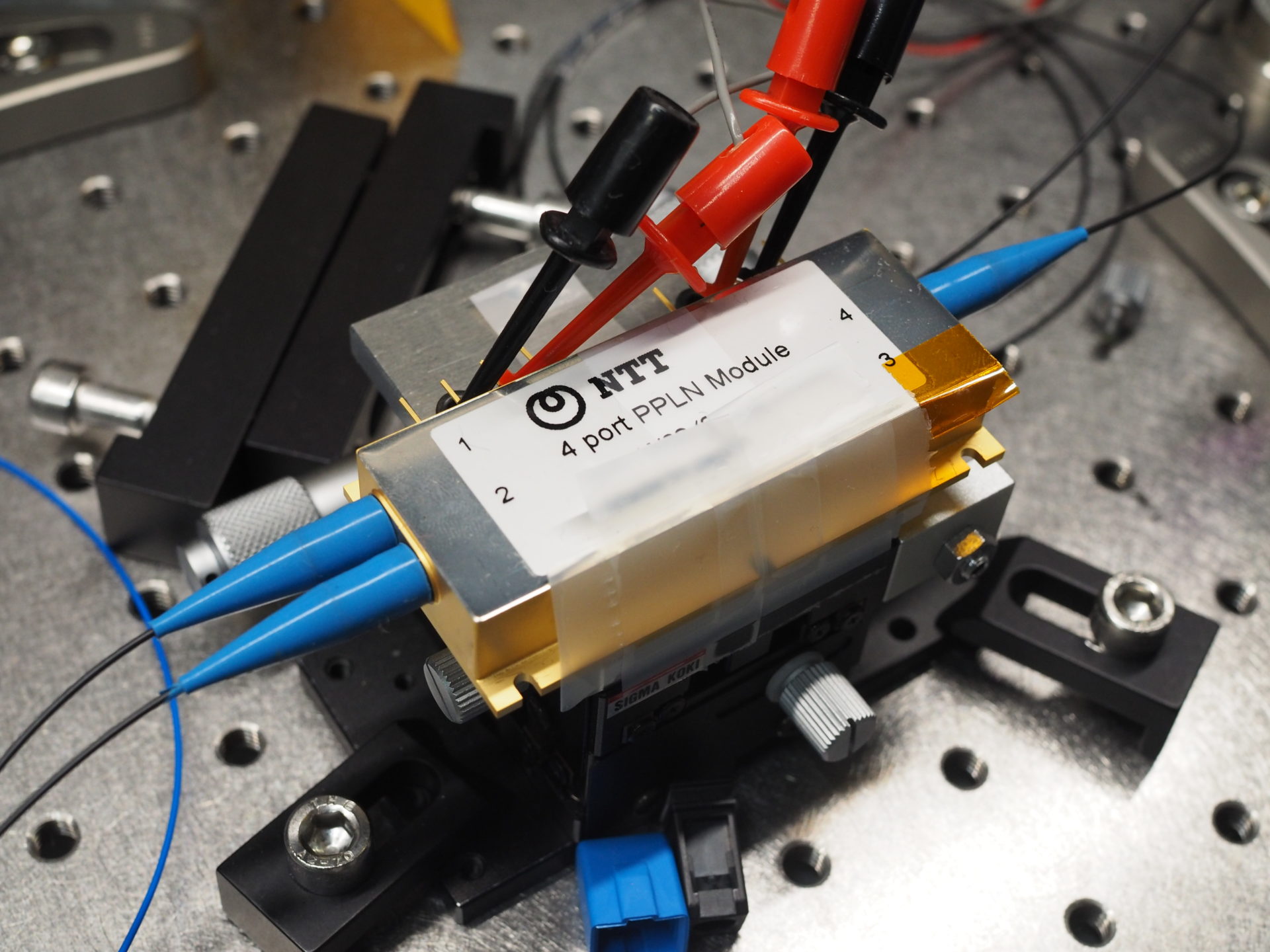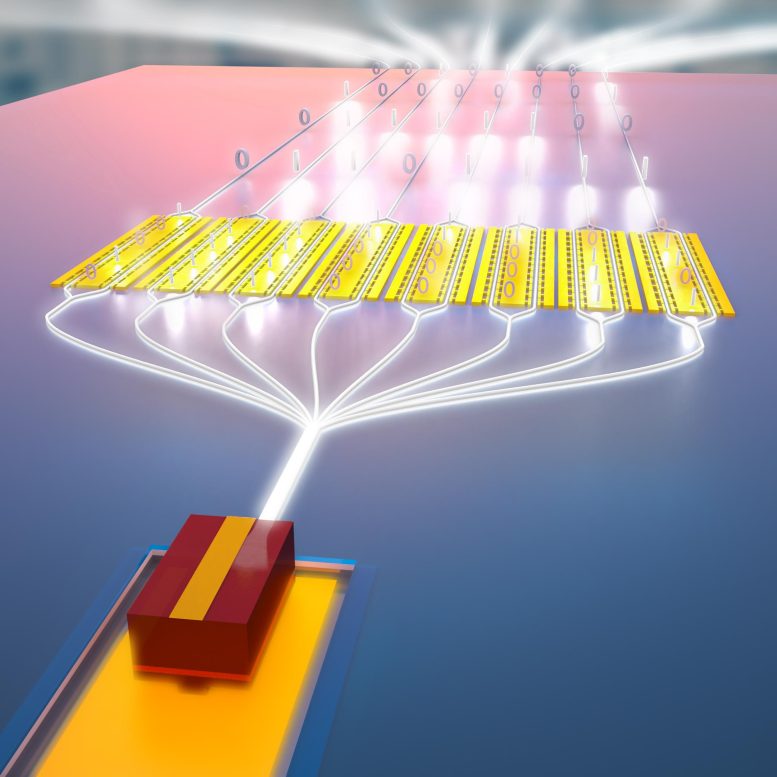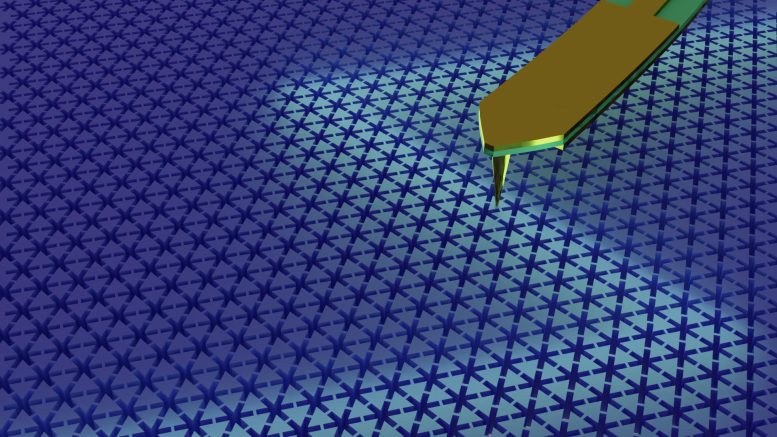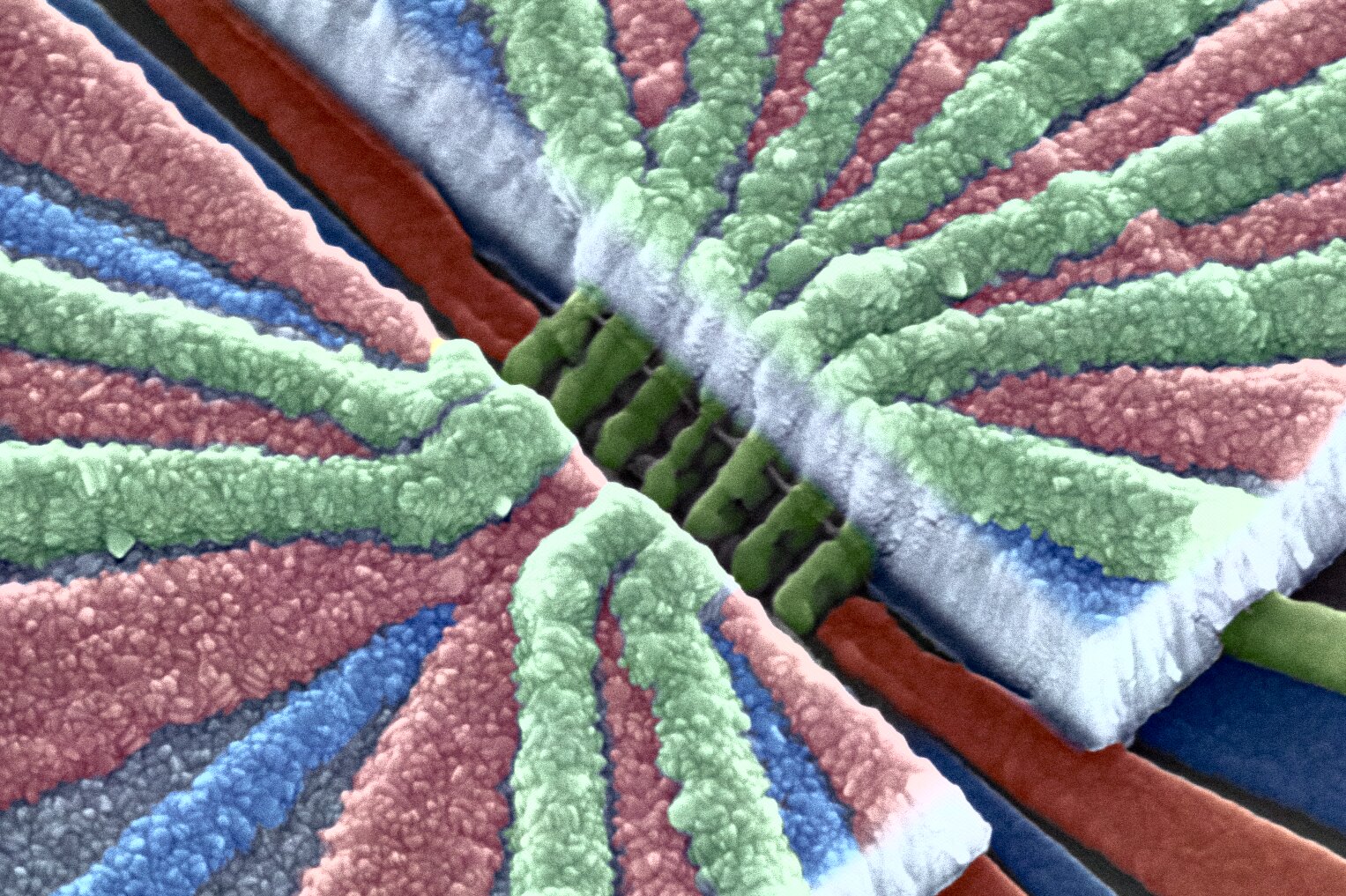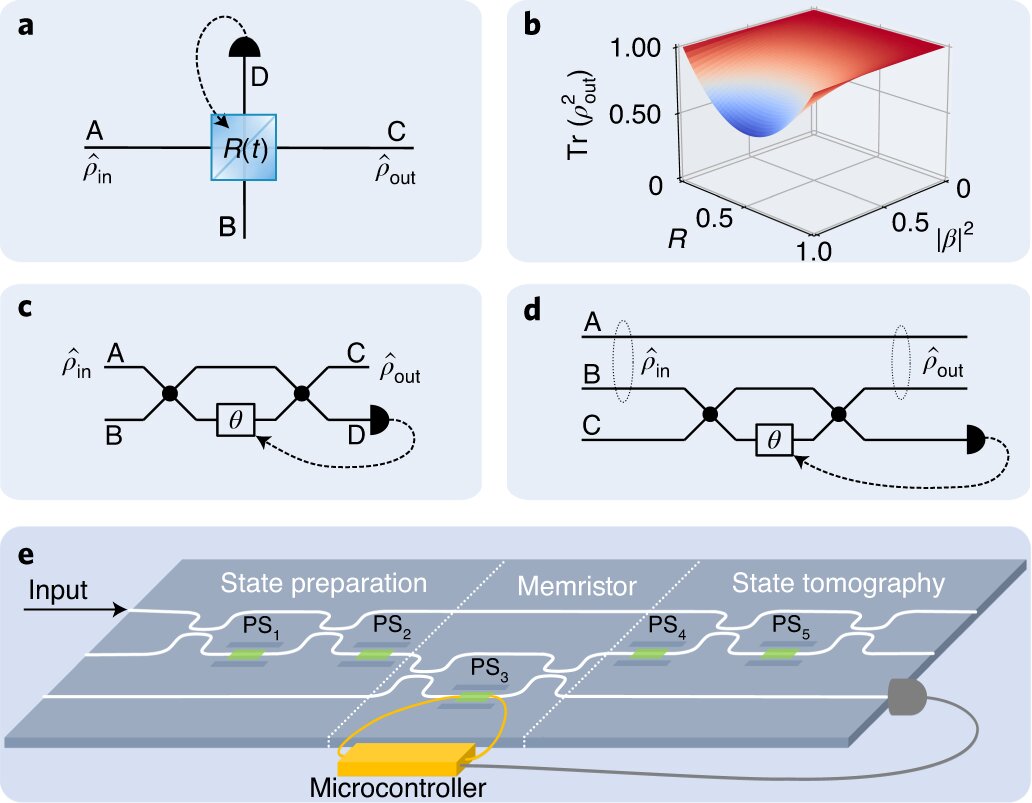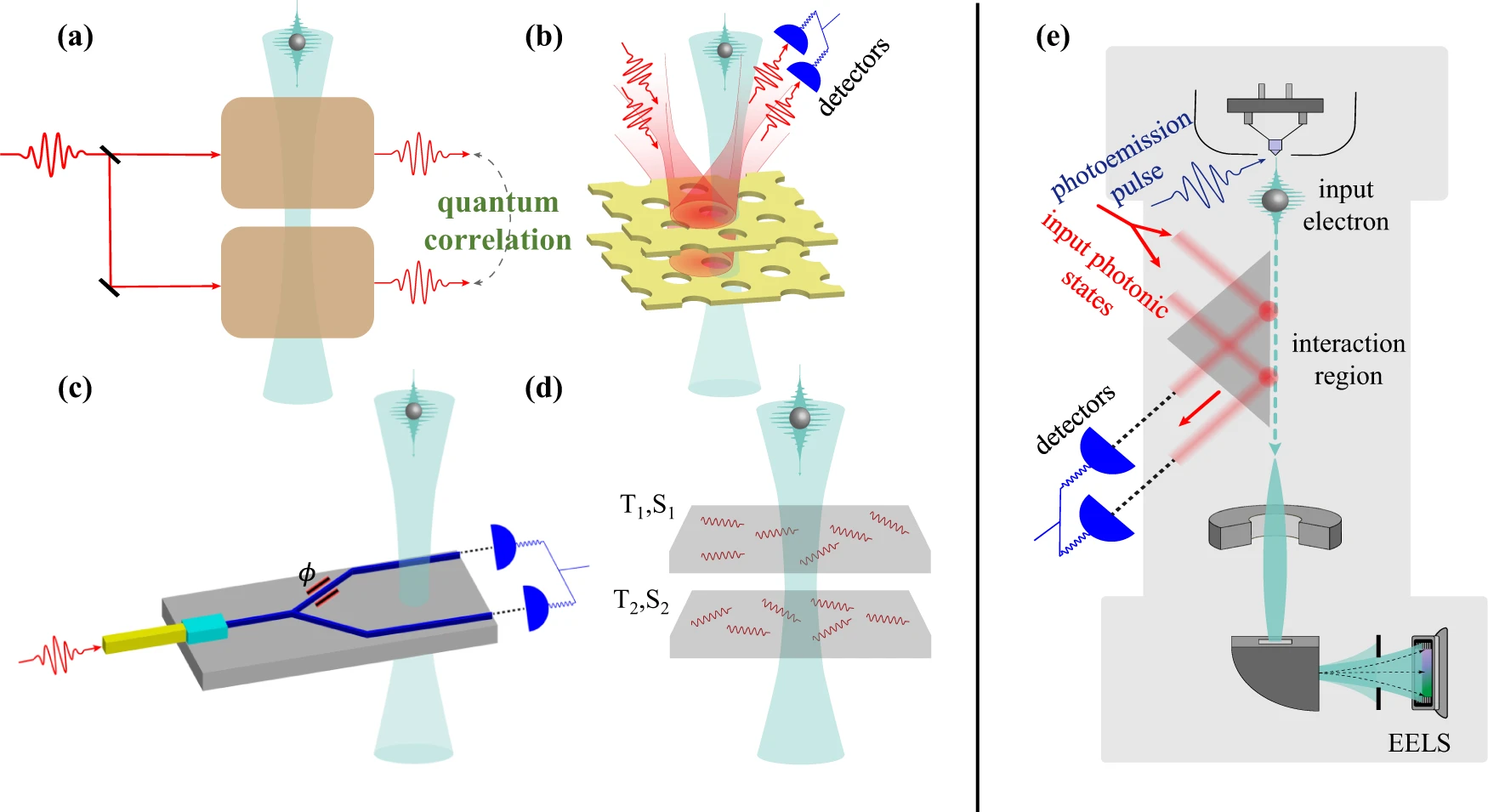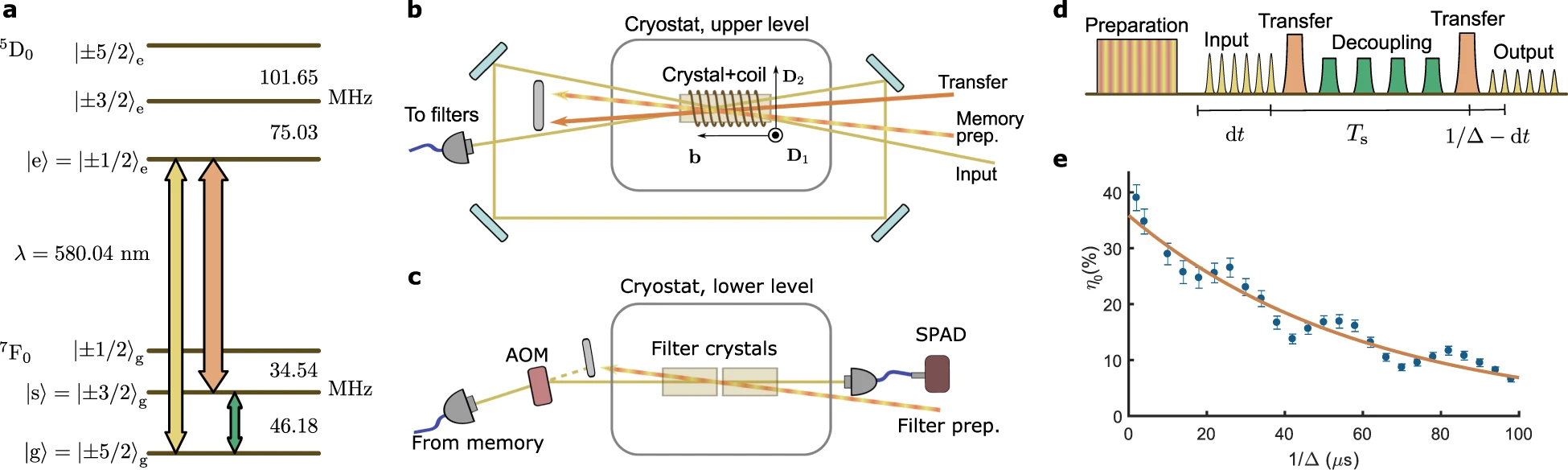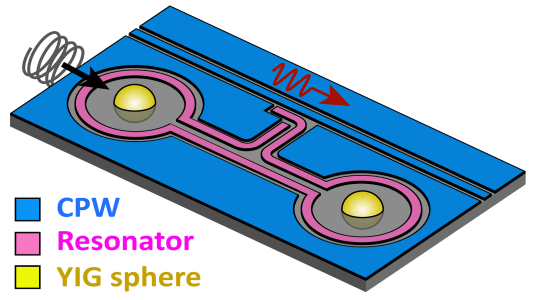
Hybrid qubit based on topological insulators
With their superior properties, topological qubits could help achieve a breakthrough in the development of a quantum computer designed for universal applications. So far, no one has yet succeeded in unambiguously demonstrating a quantum bit, […]