Light-Based Quantum Networks: A Breakthrough in Secure Data
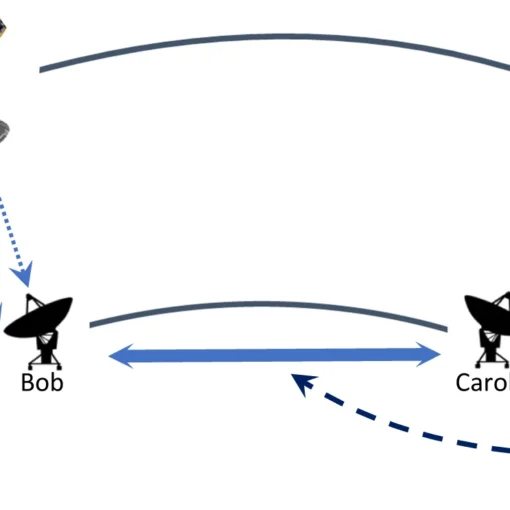
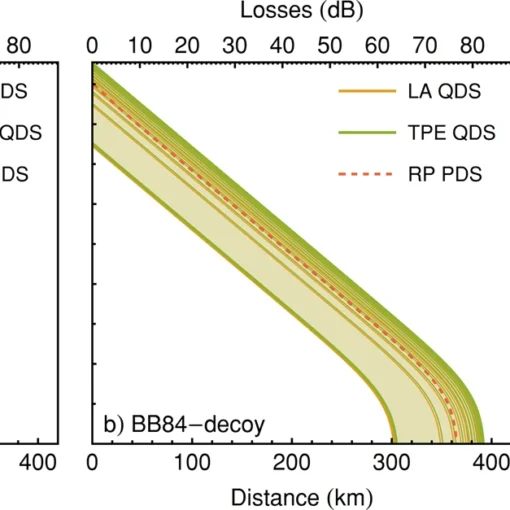
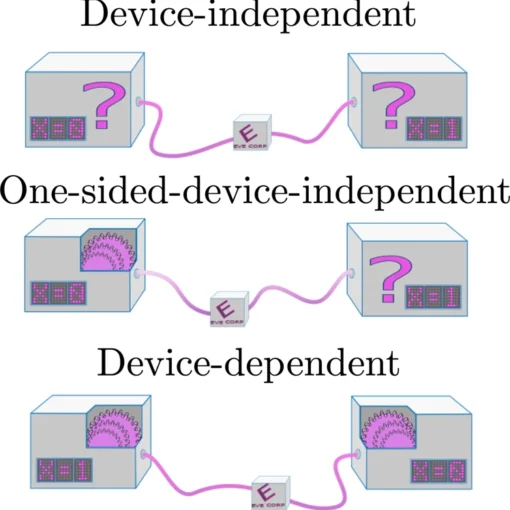
Scientists at Leibniz University Hannover have developed a cost-effective quantum network security system using frequency-bin coding of light particles, which reduces complexity and equipment costs by 75% while enhancing security against quantum computer threats through a simplified single-detector design that enables dynamic, scalable quantum key distribution.