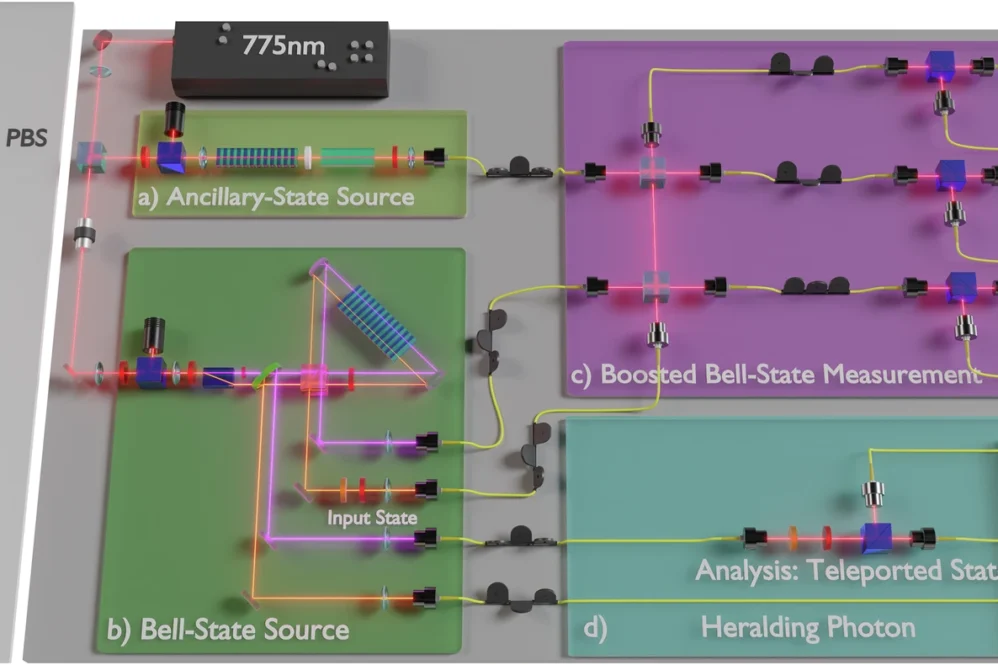
This breakthrough research elegantly overcomes one of quantum teleportation’s fundamental limitations. For years, quantum teleportation has offered tremendous potential for secure communications and advanced computing, but its practical implementation has been hampered by the 50% success ceiling of Bell-state measurements using linear optics.
The researchers have shattered this barrier by introducing ancillary photonic states that interfere with Bell states. This ingenious approach achieved an impressive average fidelity of 0.8677 ± 0.0024 for the teleported states, with an overall acceptance rate of 69.71 ± 0.75% – significantly surpassing the previous 50% limit.
What makes this work particularly significant is its practical focus. Rather than merely verifying pre-prepared Bell states, the team demonstrated boosted Bell-state projections on arbitrary input states from independent sources. This represents the first real-world test of Boosted Quantum Teleportation’s viability for practical applications.
The implications extend far beyond simple point-to-point communications. This enhanced teleportation efficiency could revolutionize quantum repeaters, which are essential for extending quantum communication over long distances. It also holds promise for measurement-based quantum computation, where teleportation-like operations form the backbone of information processing.
The researchers’ approach maintains the advantages of linear-optical implementations – experimental simplicity and robustness – while circumventing their traditional limitations. By using ancillary two-photon states, they’ve demonstrated that the probability of conclusive projective measurements on the Bell-state basis can be significantly increased.
This work represents an important milestone in making quantum teleportation practical for real-world applications. It suggests that with current technology, using ancillary photons to boost quantum protocols based on teleportation is viable, potentially accelerating progress in quantum networks, secure communications, and distributed quantum computing. The full characterization of the quantum channel provides valuable data for future implementations, while maintaining compatibility with existing photonic quantum technologies, offering a clear pathway toward scalable quantum information processing systems.
Reference: D’Aurelio, S.E., Bayerbach, M.J. & Barz, S. Boosted quantum teleportation. npj Quantum Inf 11, 37 (2025). doi:10.1038/s41534-025-00992-4