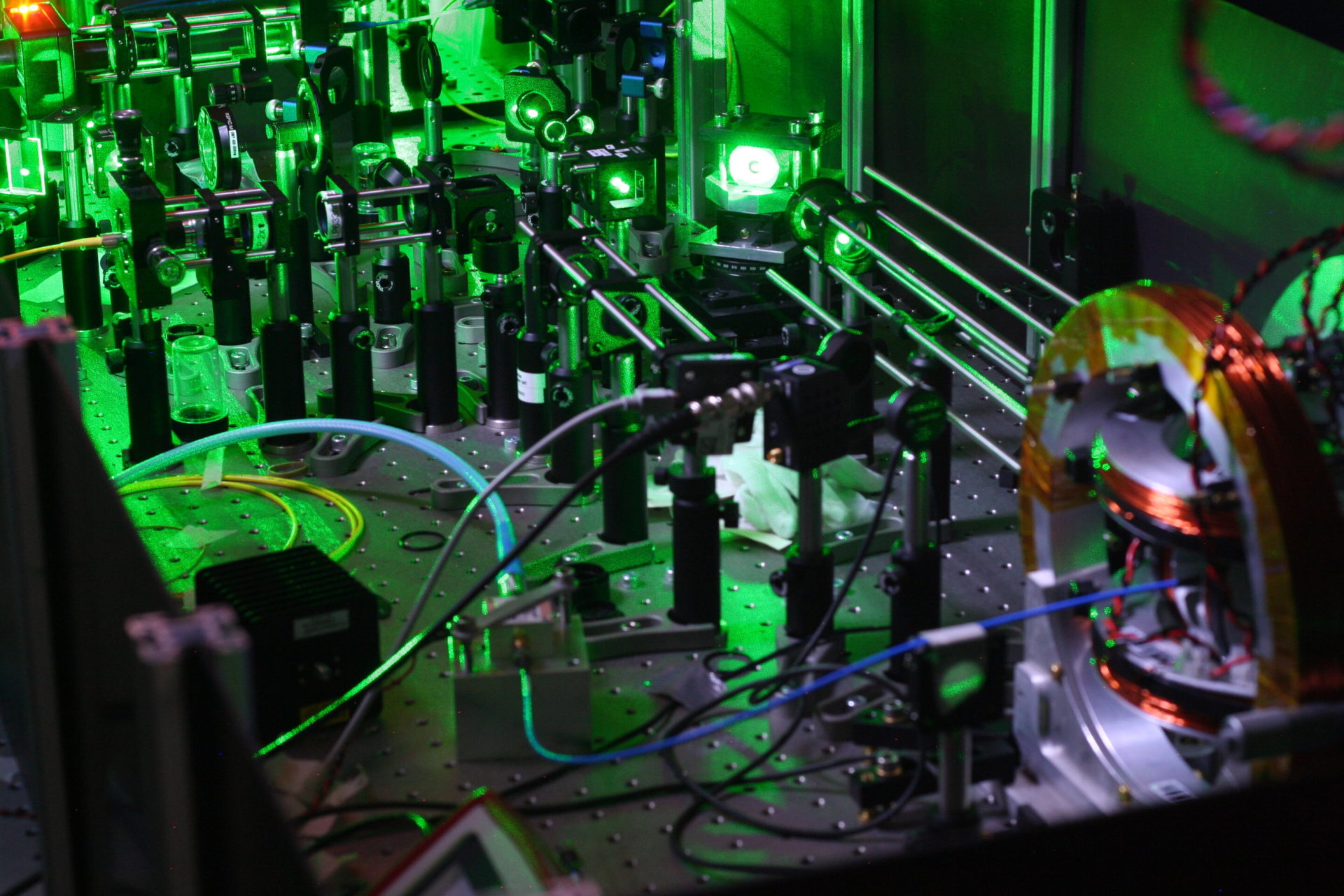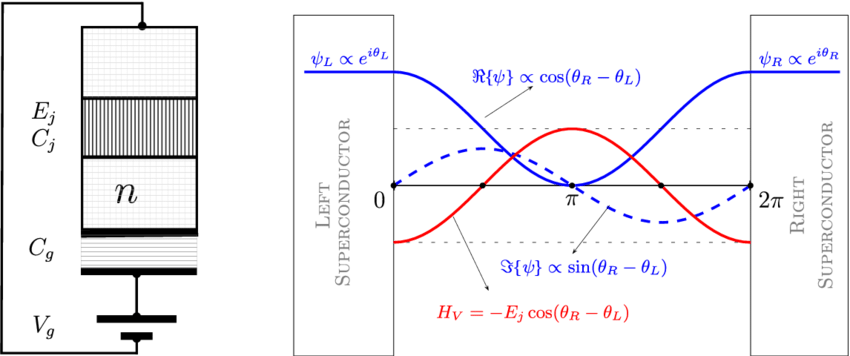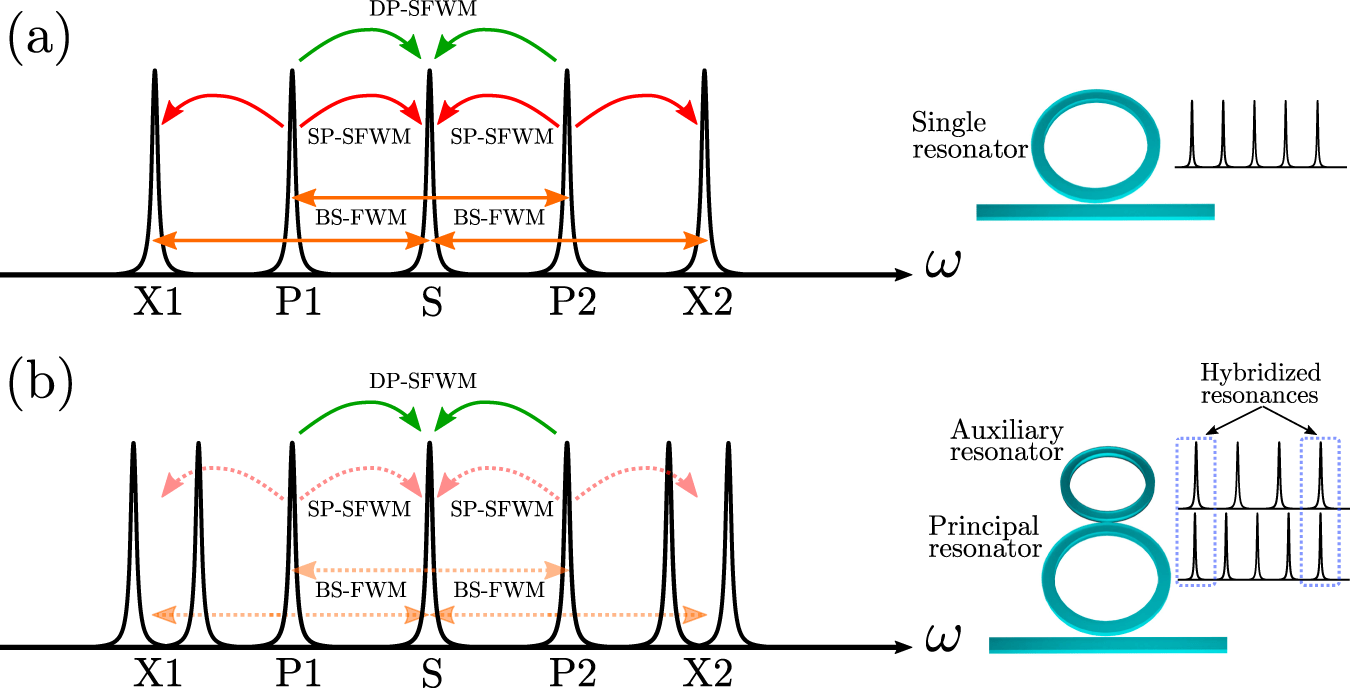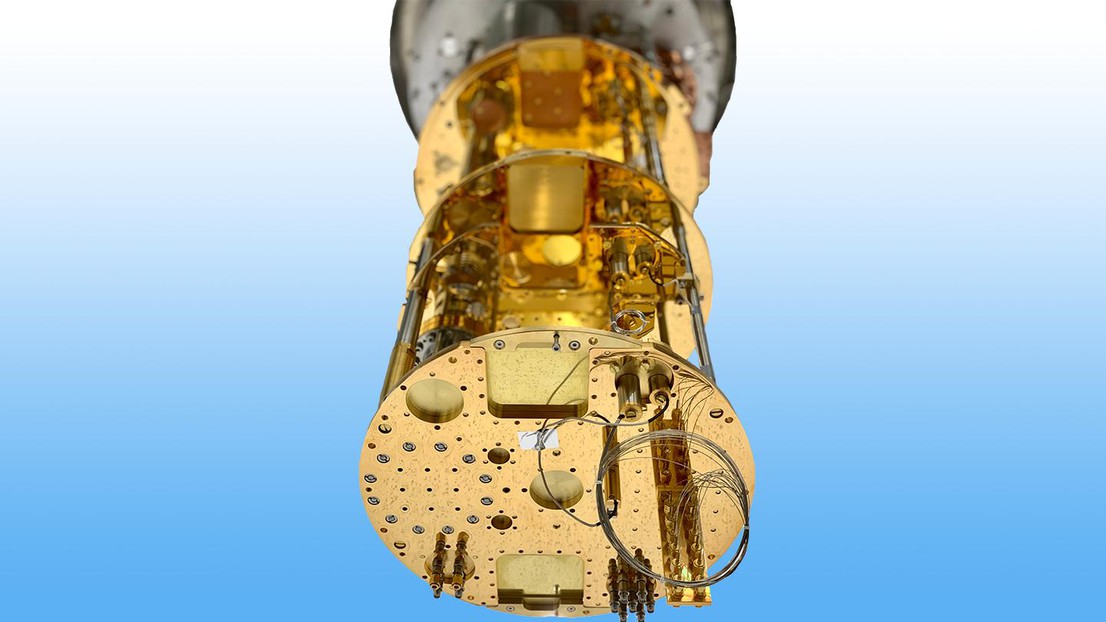
Light meets superconducting circuits
Researchers in the group of Professor Tobias J. Kippenberg at EPFL’s School of Basic Sciences have now developed a novel approach that uses light to read out superconducting circuits, thus overcoming the scaling challenges of […]