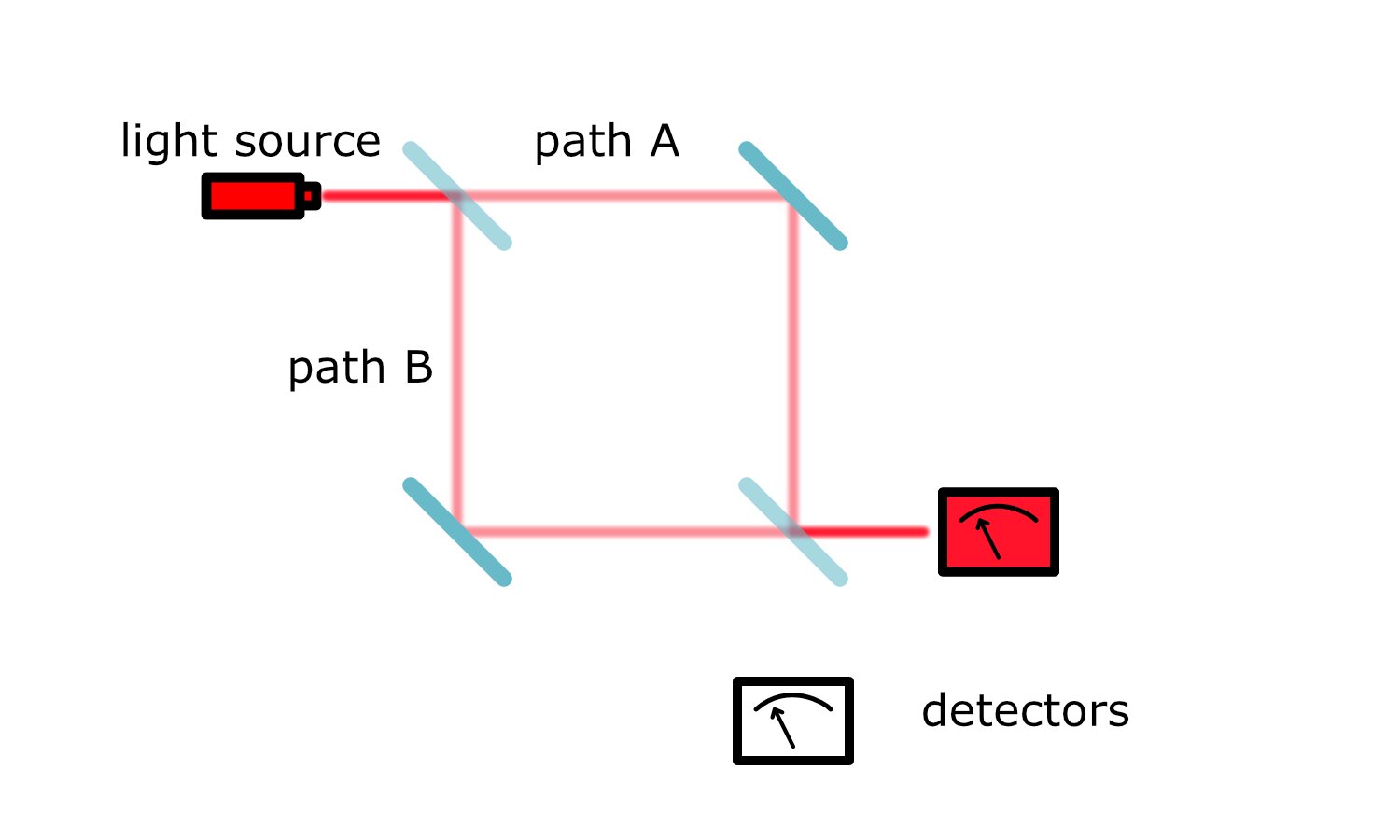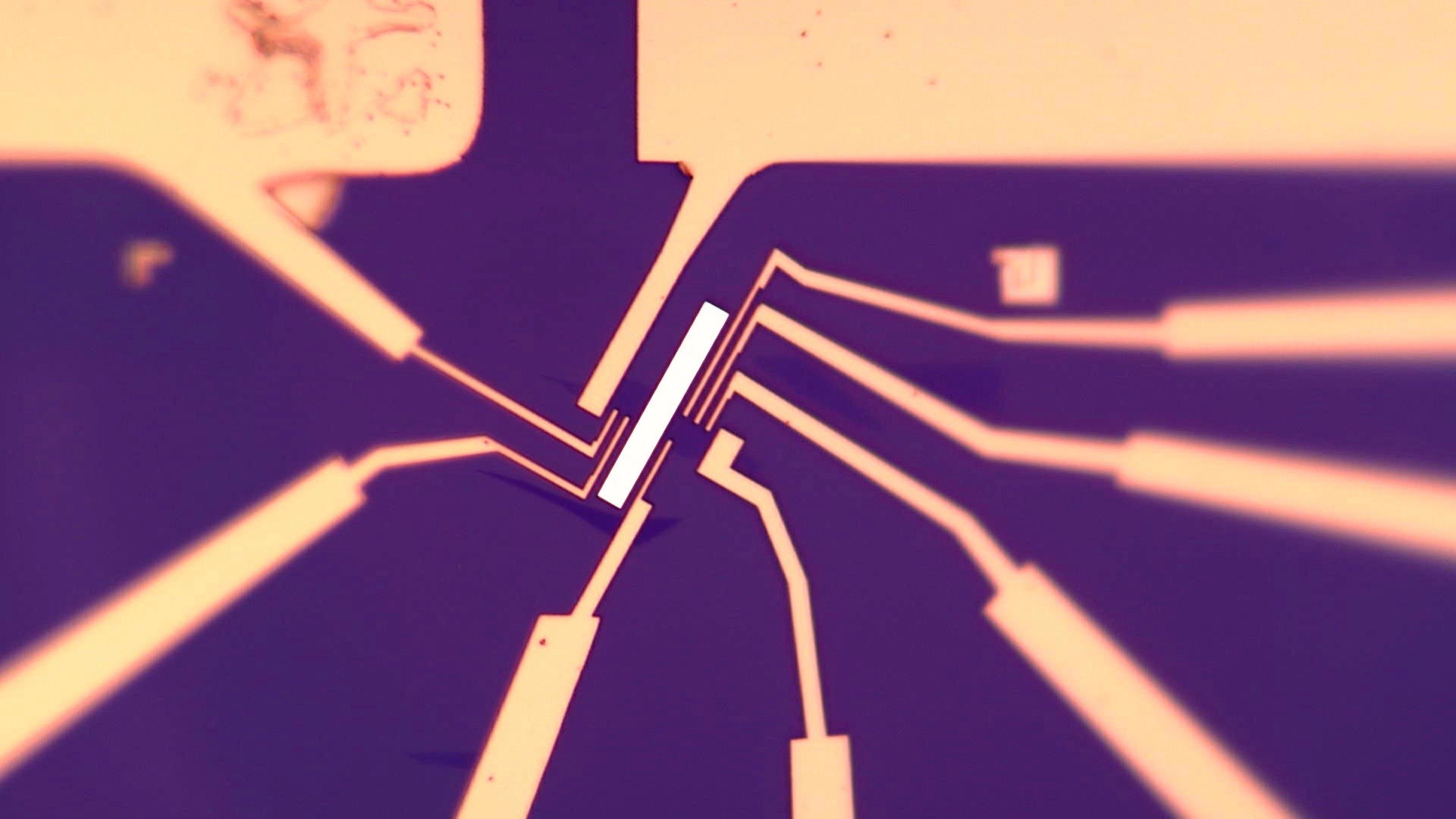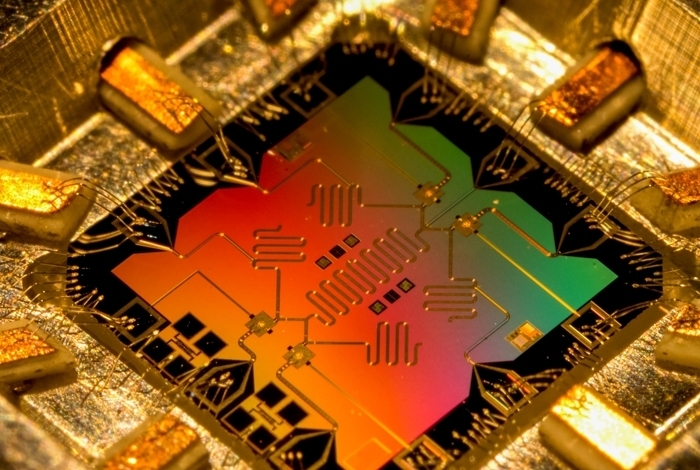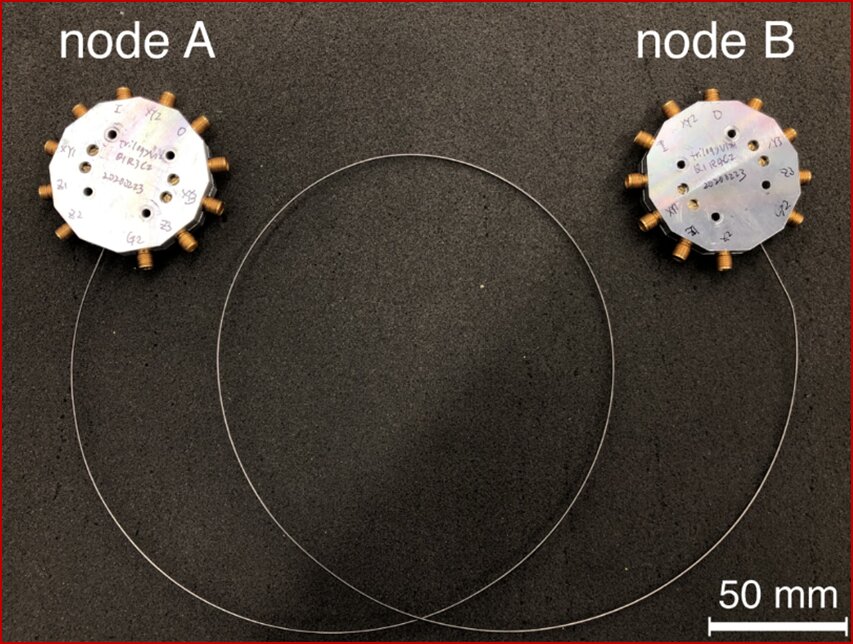
A protocol to explore entanglement dynamics via spacetime duality
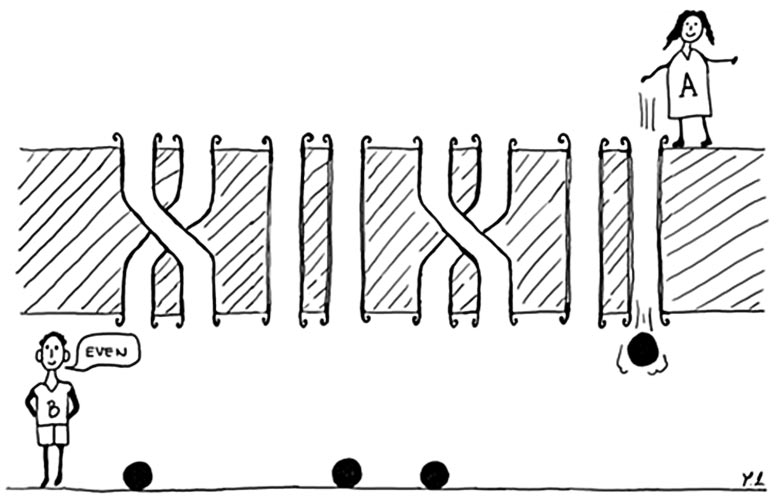
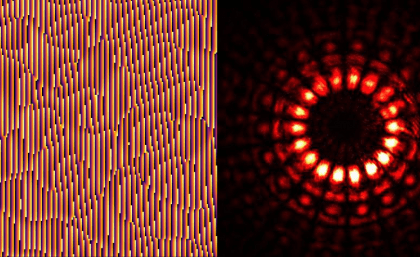
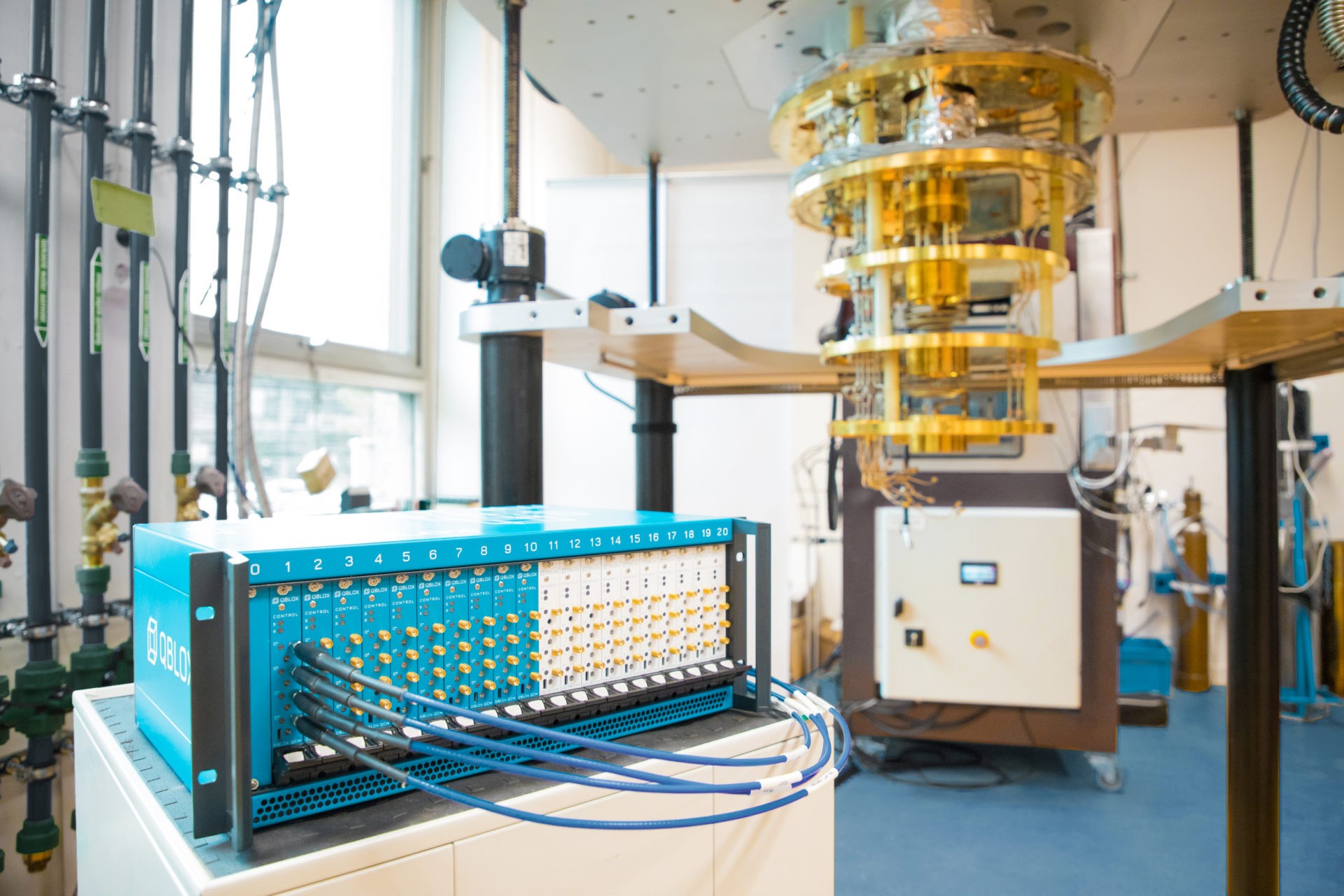
Researchers at Stanford University have recently carried out a study exploring the role of quantum measurements in many-body dynamics. They specifically presented a protocol that can be used to realize dynamics that include quantum measurements […]