A joint group of scientists has demonstrated that temperature difference can be used to entangle pairs of electrons in superconducting structures.
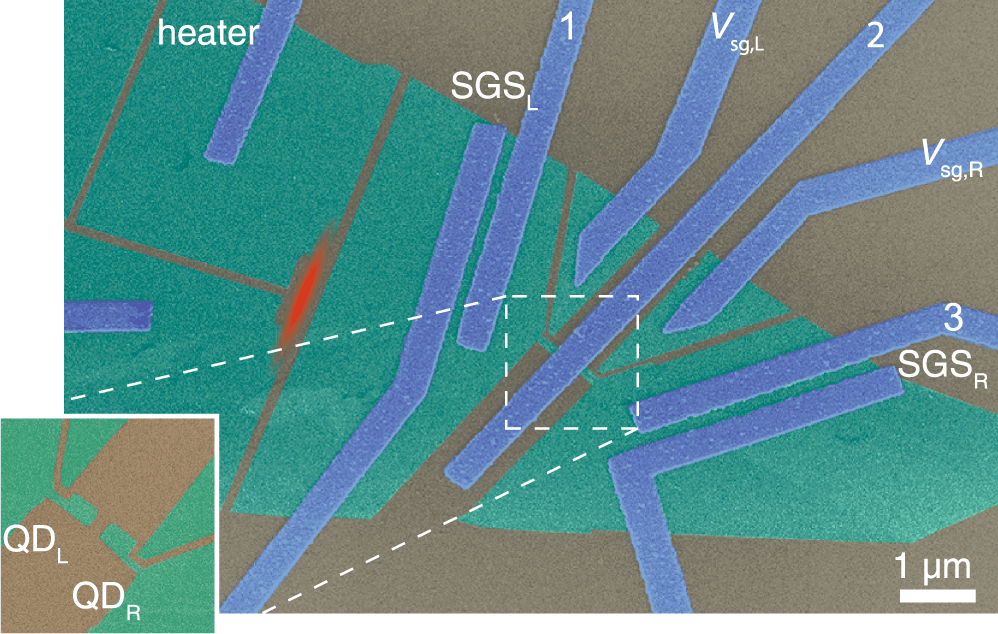
The researchers designed a device where a superconductor was layered withed graphene and metal electrodes. Superconductivity is caused by entangled pairs of electrons called Cooper pairs. Using a temperature difference, they cause them to split, with each electron then moving to different normal metal electrode.
The experiment has shown that the process of Cooper pair splitting works as a mechanism for turning temperature difference into correlated electrical signals in superconducting structures.
The experimental discovery promises powerful applications in quantum devices. (Aalto University)
The paper has been published in Nature Communications.
The post Electrons entanglement using heat appeared first on Swiss Quantum Hub.