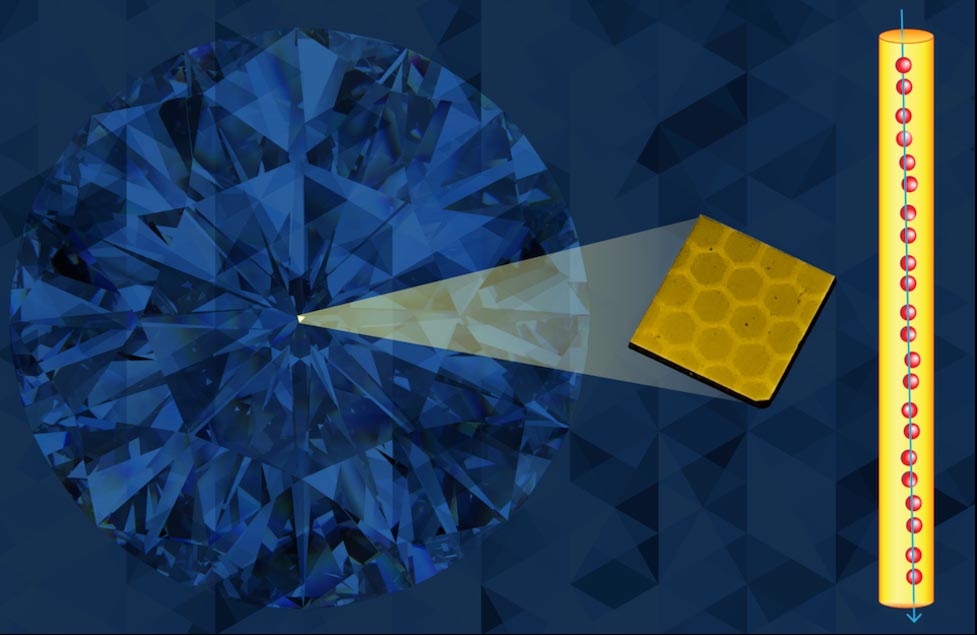
A Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory-led international team of researchers has discovered a way to use ion beams to create long strings of “color center” qubits in diamond.
Creating large numbers of high-quality qubits, in close enough proximity for coupling to each other, is one of the great challenges of quantum computing. The team has been exploring the use of ion beams to create artificial color centers in diamond for use as qubits.
When swift (high-energy) heavy ions such as the beams this team used – gold ions with a kinetic energy of about one billion electron volts – pass through a material, such as nitrogen-doped diamond, they leave a trail of nitrogen-vacancy centers along their tracks. Color centers were found to form directly, without need for further annealing (heat treatment). What’s more, they formed all along the ion tracks, rather than only at the end of the ion range as had been expected from earlier studies with lower-energy ions. In these straight “percolation chains,” color-center qubits are aligned over distances of tens of microns, and are just a few nanometers from their nearest neighbors. A technique developed by Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry measured color centers with depth resolution.
Results published in the current article show that it will be possible to form quantum registers with up to about 10,000 coupled qubits – two orders of magnitude greater than achieved thus far with the complementary technology of ion-trap qubits – over a distance of about 50 microns (about the width of a human hair). (SciTechDaily)
Their work has been published in the journal Applied Physics Letters.