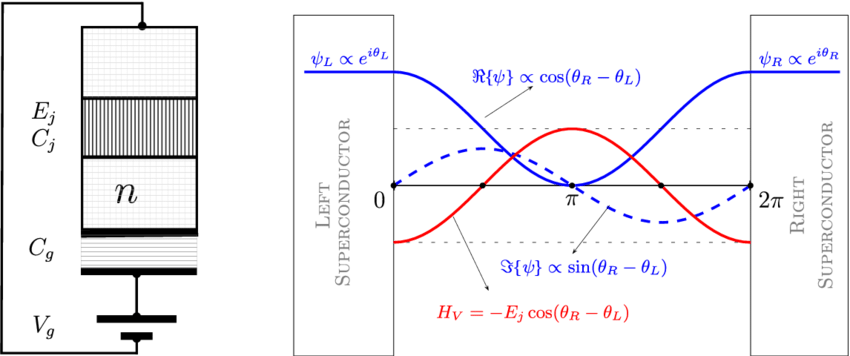
Josephson junctions are simple superconducting devices comprising an insulator or semiconductor separating two superconducting regions. They form the workhorse of superconducting technologies and are exquisitely sensitive to magnetic field.
One long-sought proposal has been to use these devices to detect light.
Although device performance can be degraded by the generation of quasiparticles formed from broken Cooper pairs, this phenomenon also opens opportunities to sensitively detect electromagnetic radiation.
Researchers have realized a photosensitive Josephson junction based on graphene that is capable of sensing single infrared photons.
Such a photosensitive Josephson junction is expected to operate as a high-speed, low-power consumption optical interconnect for communication between superconducting-based supercomputers and quantum computers.
The paper has been published in Nature.