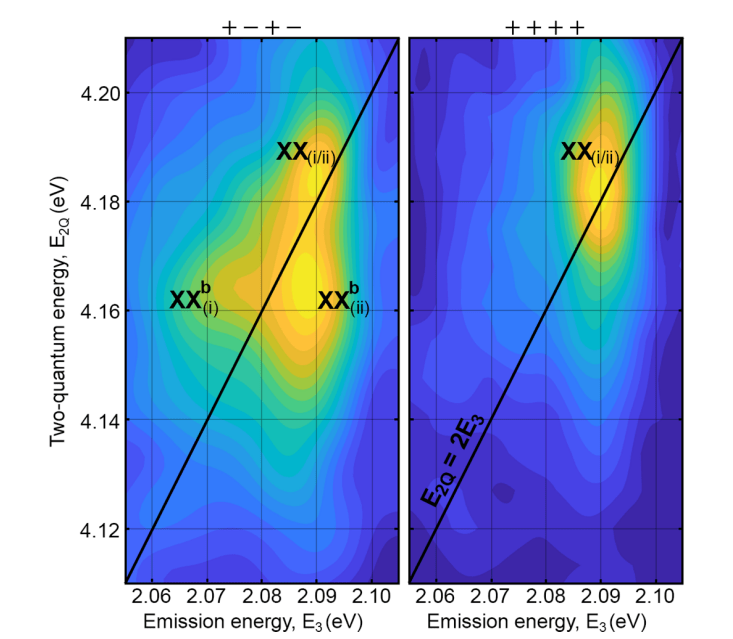
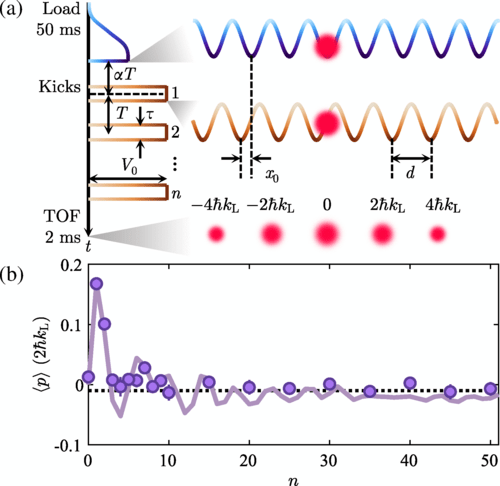
Antiprotons in superfluid: a new way for sensitive measurements of antimatter
A team of scientists at CERN led by MPQ physicist Masaki Hori has found that a hybrid antimatter-matter atom behaves in an unexpected way when submerged in superfluid helium. The result may open a new […]