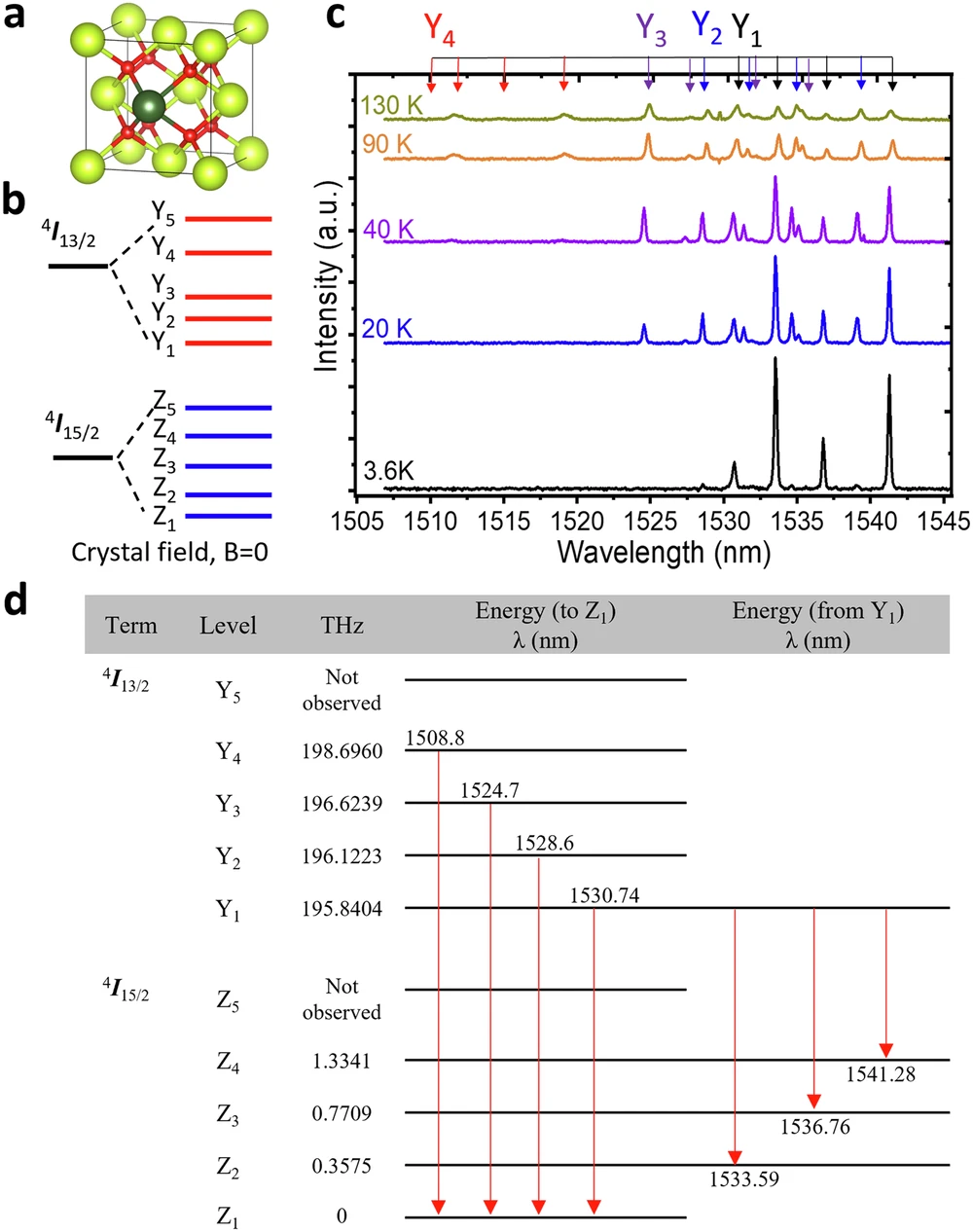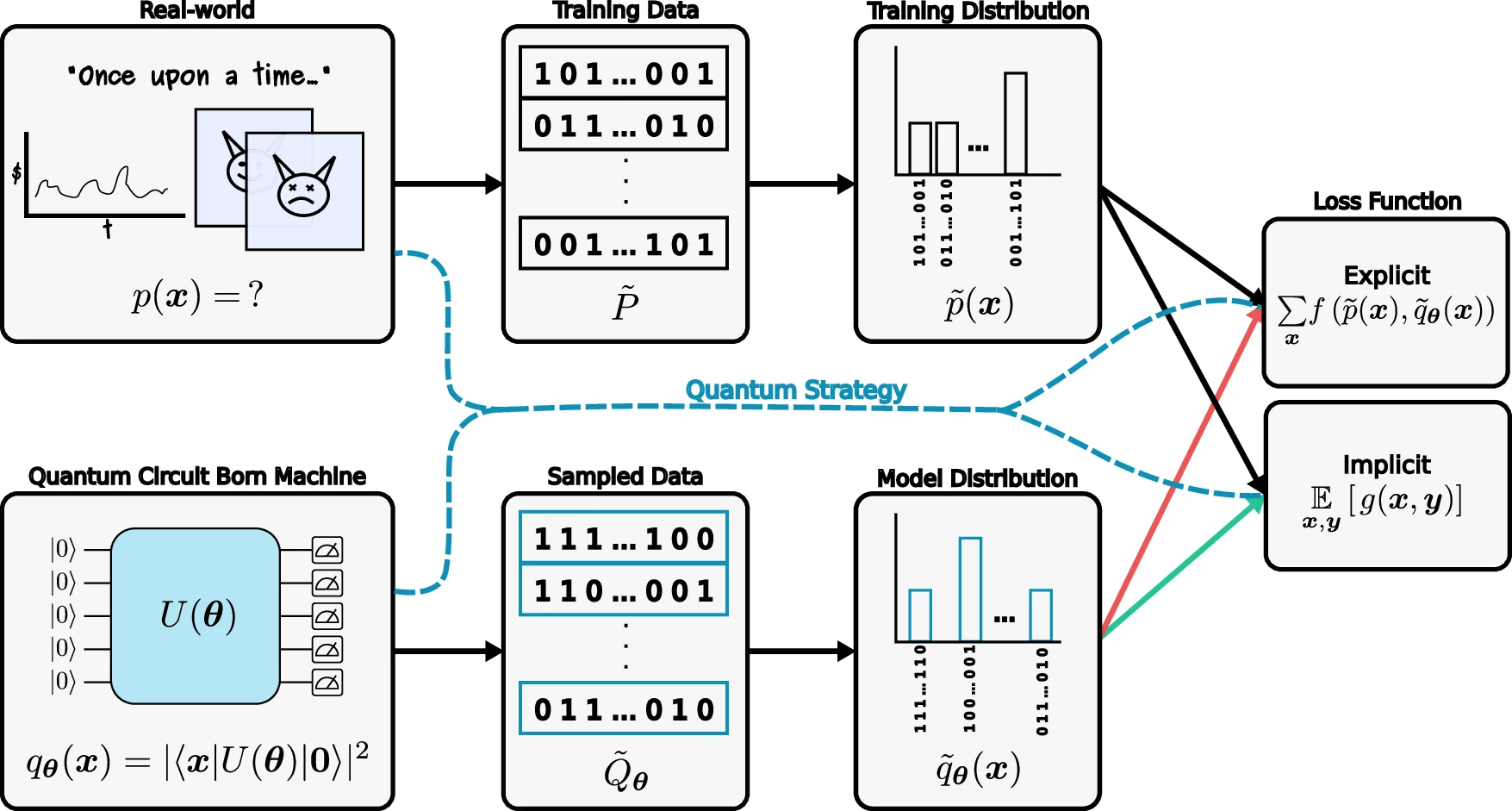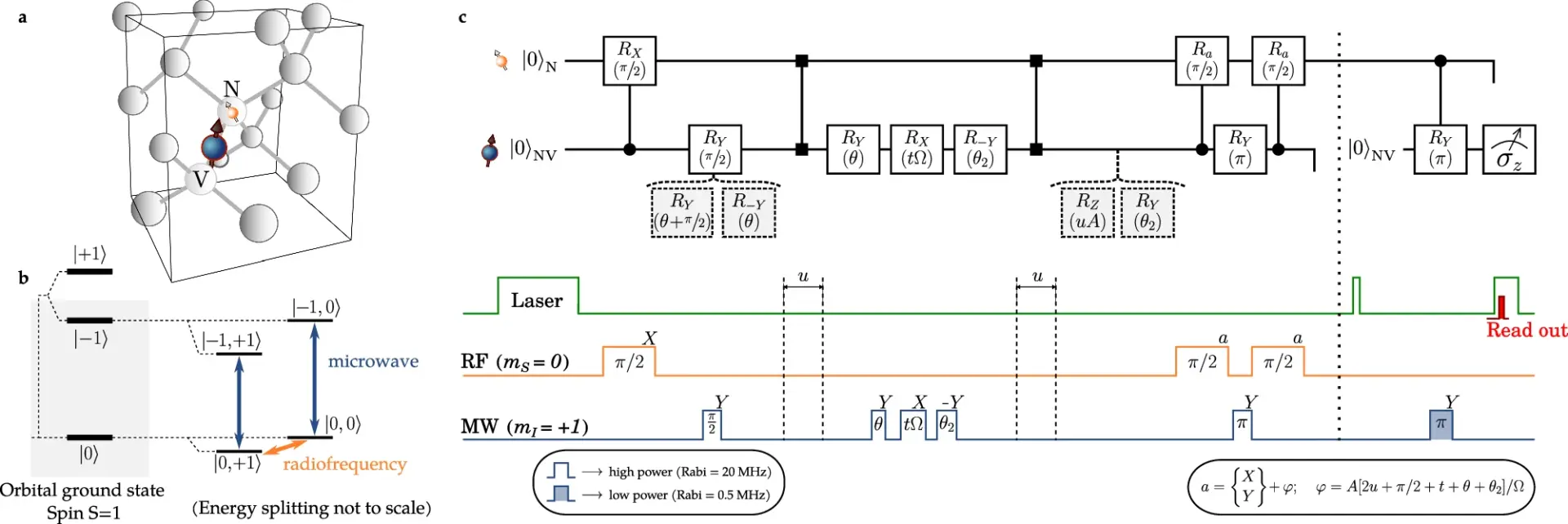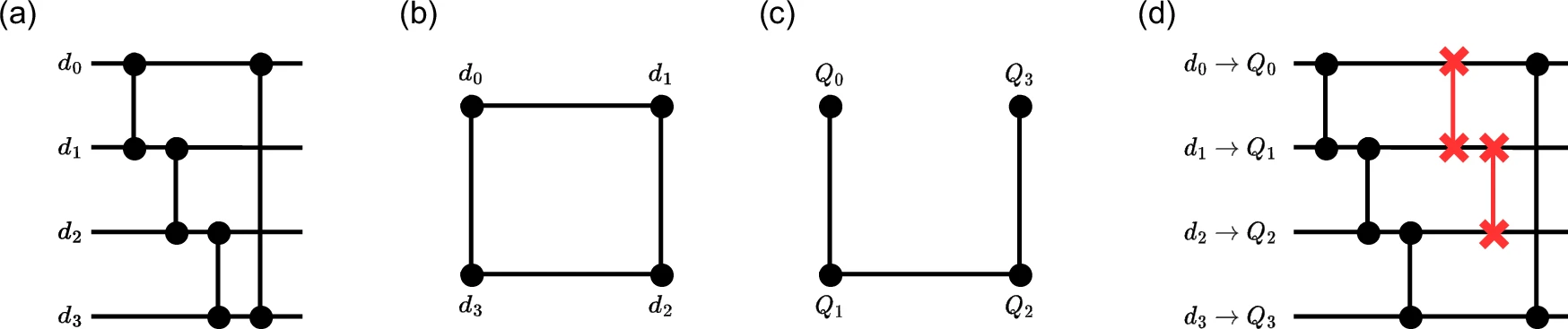
Local testability of distance-balanced quantum codes
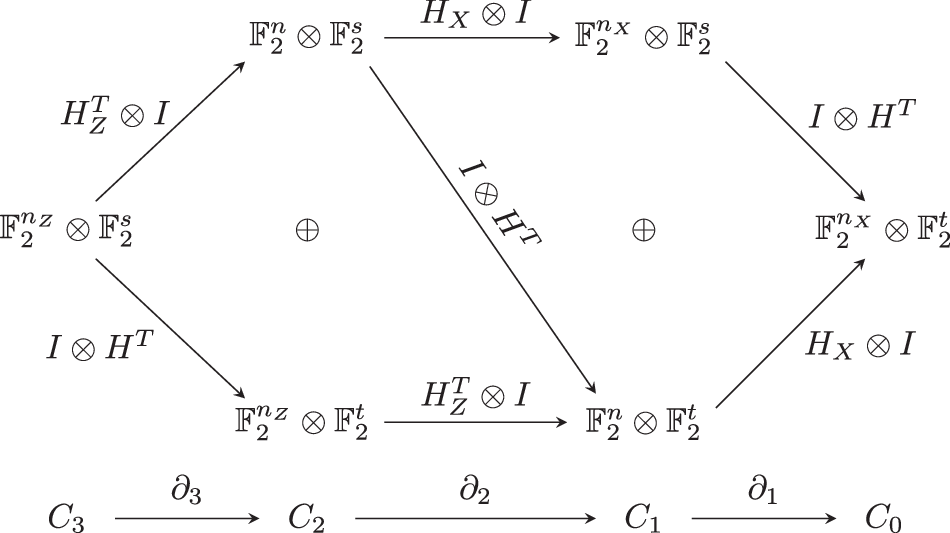
npj Quantum Information, Published online: 20 November 2024; doi:10.1038/s41534-024-00908-8 In this paper, scientists proved a lower bound on the soundness of quantum locally testable codes under the distance balancing construction of Evra et al. Their […]