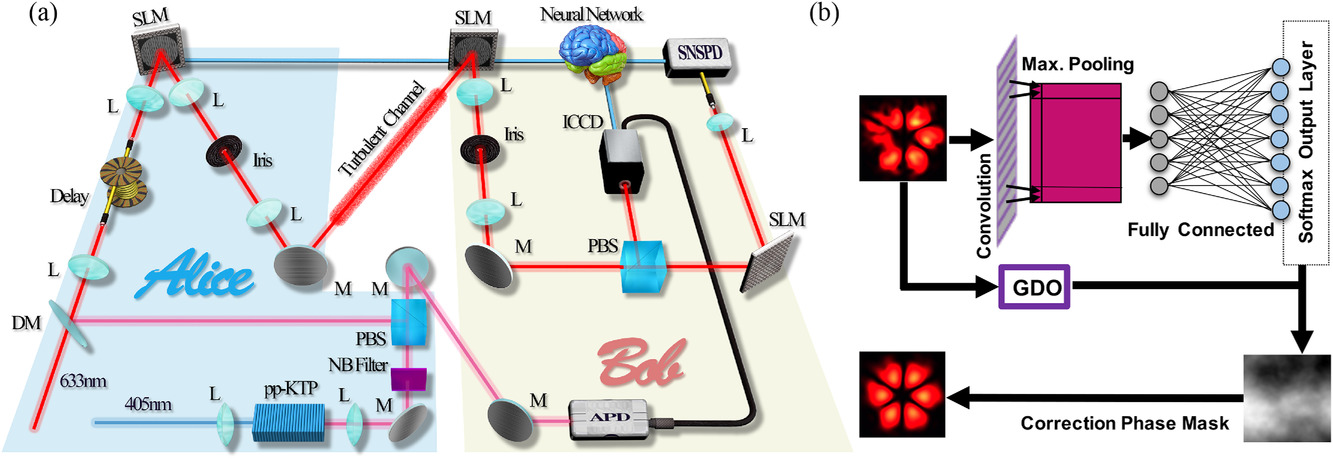
Researchers from Louisiana State University have introduced a smart quantum technology for the spatial mode correction of single photons. The team has exploited the self-learning and self-evolving features of artificial neural networks to correct the distorted spatial profile of single photons.
Spatial modes of light constitute valuable resources for a variety of quantum technologies ranging from quantum communication and quantum imaging to remote sensing. Nevertheless, their vulnerabilities to phase distortions, induced by random media, impose significant limitations on the realistic implementation of numerous quantum-photonic technologies. Unfortunately, this problem is exacerbated at the single-photon level. Over the last two decades, this challenging problem has been tackled through conventional schemes that utilize optical nonlinearities, quantum correlations, and adaptive optics. In this article, the self-learning and self-evolving features of artificial neural networks are exploited to correct the complex spatial profile of distorted Laguerre–Gaussian modes at the single-photon level. Furthermore, the potential of this technique is used to improve the channel capacity of an optical communication protocol that relies on structured single photons. The results have important implications for real-time turbulence correction of structured photons and single-photon images.
The newly developed technique boosts the channel capacity of optical communication protocols that rely on structured photons. (Phys.org)
The paper has been published in Advanced Quantum Technologies.