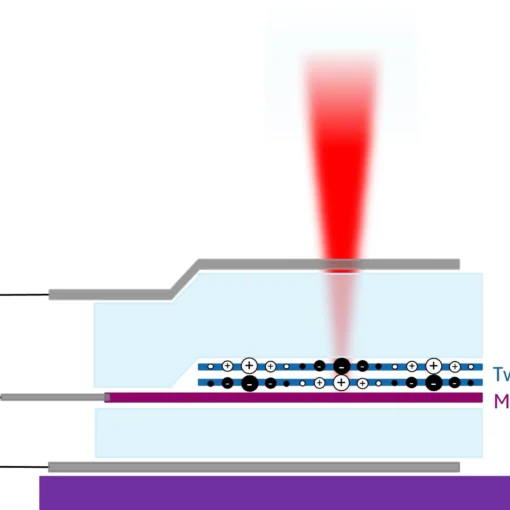
Harnessing Coulomb Interactions in Nanoscale Ferroelectric Moiré Structures
Researchers created a nanoscale ferroelectric moiré pattern using hexagonal boron nitride layers to generate a purely electrostatic potential that enhances Coulomb interactions in transition metal dichalcogenides, enabling optical detection of electron correlations and ordered states while opening pathways to explore exotic quantum phenomena like chiral layer-pseudospin liquids and kinetic magnetism.