Quantum Dots Unlock Majorana States for Stable Computing
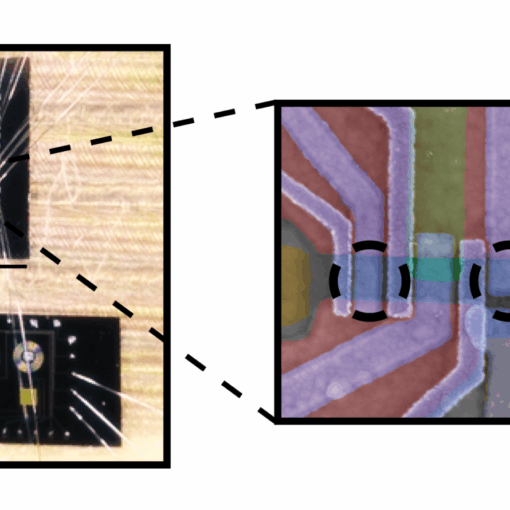
QuTech researchers in Delft created a controlled system of three quantum dots that successfully demonstrated the properties of Majorana bound states—exotic quantum particles that could enable more stable quantum computing through their unique ability to be manipulated and moved between locations while maintaining resistance to errors.
