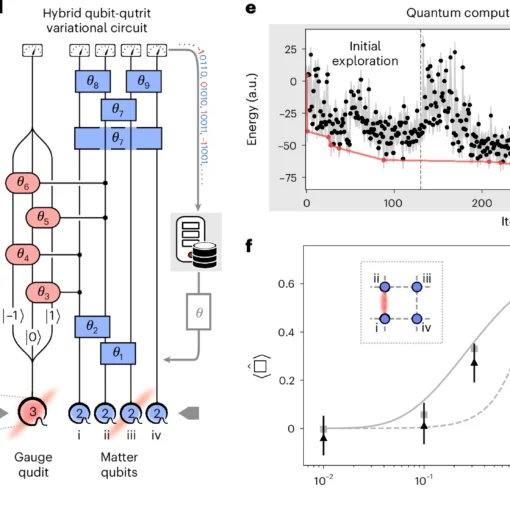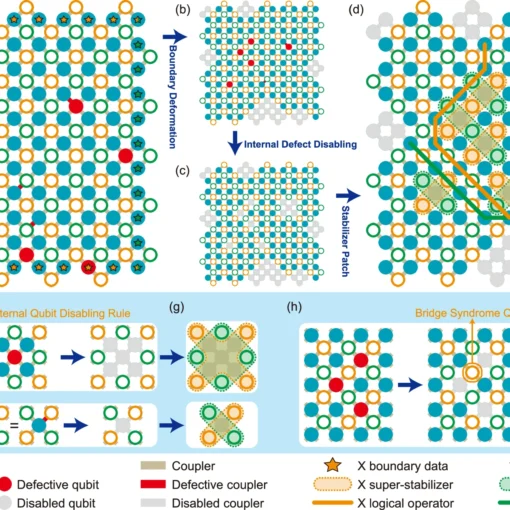
Adapting Surface Codes for Quantum Error Correction on Defective Lattices
The new automated “bandage-like” super-stabilizer approach for implementing surface codes on defective quantum lattices significantly outperforms previous methods by reducing disabled qubits by one-third and increasing code distance by 63% for a 2% defect rate, providing a crucial low-overhead solution for scaling up fault-tolerant quantum computing.