Smart quantum technologies for secure communication
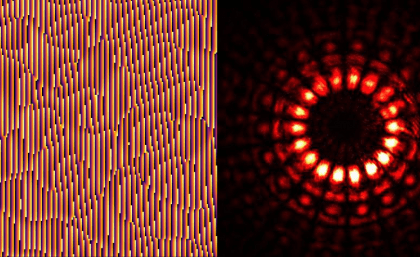
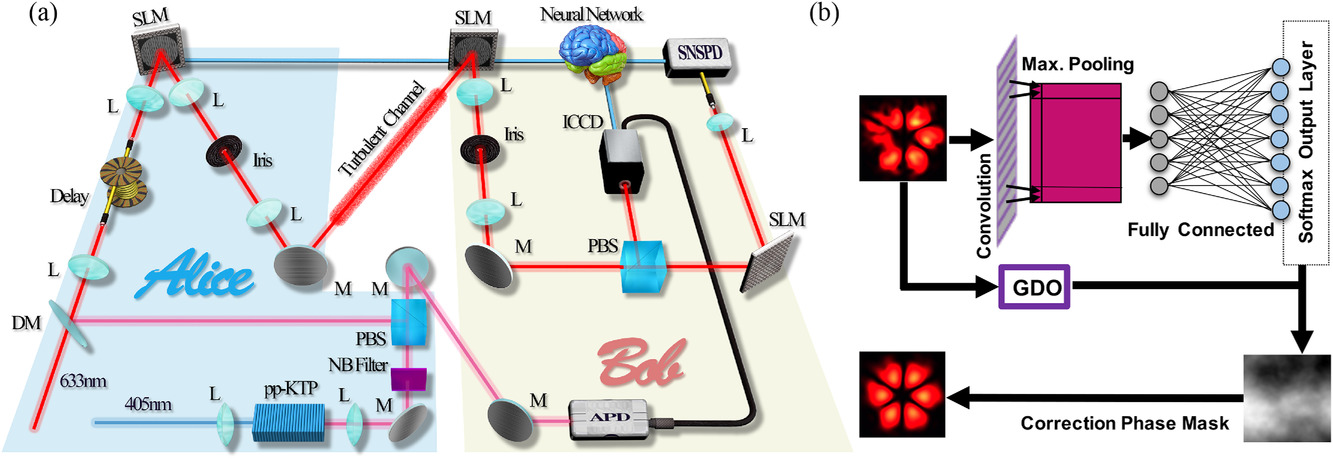
Researchers from Louisiana State University have introduced a smart quantum technology for the spatial mode correction of single photons. The team has exploited the self-learning and self-evolving features of artificial neural networks to correct the distorted spatial profile of single photons.